
Irregular sleep patterns linked to harmful gut bacteria, study suggests
Irregular sleep patterns may be linked to harmful bacteria in your gut, new research suggests. The study is the first to find multiple associations between social jet lag – the shift in internal body clock when sleeping patterns change between workdays and free days – and diet quality, diet habits, inflammation and gut microbiome (bacteria) composition. According to the findings, even a 90-minute difference in the midpoint of sleep – half-way between sleep time and wake-up time – can encourage microbiome that has negative associations with health. Previous research has suggested that working shifts disrupts the body clock and can increase risk of weight gain, heart problems and diabetes. This is the first study to show that even small differences in sleep timings across the week seems to be linked to differences in gut bacterial species Dr Wendy Hall King’s College London However, according to researchers from King’s College London there is less awareness that the body’s biological rhythms can be affected by smaller inconsistencies in sleeping patterns. This is due to people working regular hours waking early with an alarm clock on workdays compared to waking naturally on non-workdays. Senior author Dr Wendy Hall from King’s College London, said: “We know that major disruptions in sleep, such as shift work, can have a profound impact on your health. “This is the first study to show that even small differences in sleep timings across the week seems to be linked to differences in gut bacterial species. “Some of these associations were linked to dietary differences but our data also indicates that other, as yet unknown, factors may be involved. “We need intervention trials to find out whether improving sleep time consistency can lead to beneficial changes in the gut microbiome and related health outcomes.” First author Kate Bermingham, from King’s College London and senior nutrition scientist at ZOE, said: “Sleep is a key pillar of health, and this research is particularly timely given the growing interest in circadian rhythms and the gut microbiome. “Even a 90-minute difference in the mid-point of sleep can encourage microbiota species which have unfavourable associations with your health.” Researchers suggest the composition of the microbes in the gut may negatively or positively affect health by producing toxins or beneficial products. Specific species of microbes can correspond to an individual’s risk of long-term health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease and obesity. The microbiome is influenced by what food someone eats, which makes the diversity of the gut adjustable. Researchers assessed a group of 934 people from the ZOE Predict study, the largest ongoing nutritional study of its kind. They looked at blood, stool and gut microbiome samples, as well as glucose measurements in people whose sleep was irregular compared to those who had a routine sleep schedule. Unlike past research, the group consisted of mainly lean and healthy individuals with most of them getting more than seven hours sleep throughout the week. The study, published in The European Journal of Nutrition, found that just a 90-minute difference in the timing of the midpoint of sleep is associated with differences in what the gut microbiome is made up of. According to the findings, having social jet lag was associated with lower overall diet quality, higher intakes of sugar-sweetened beverages, and lower intakes of fruits and nuts. This may directly influence the abundance of specific microbiota in the gut, researchers say. Three out of the six microbiota species more abundant in the social jet lag group have what researchers describe as unfavourable associations with health. They are linked with poor diet quality, indicators of obesity and cardiometabolic health, like heart attack, stroke, and diabetes, and markers in your blood related to higher levels of inflammation and cardiovascular risk. Previous research has found social jet lag is associated with weight gain, chronic illness and mental fatigue. Dr Sarah Berry from King’s College London and chief scientist at ZOE added: “Maintaining regular sleep patterns, so when we go to bed and when we wake each day, is an easily adjustable lifestyle behaviour we can all do, that may impact your health via your gut microbiome for the better.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live N-Dubz cement comeback with first new album in 13 years Babies as young as four months have taste in fine art, study shows ADHD symptoms in children can be transformed with brain stimulation therapy
2023-08-02 17:28

Hugo Boss Guidance Upgrade Leaves Investors Wanting More
Hugo Boss AG raised its sales and profit guidance again for 2023 after second-quarter sales growth beat estimates
2023-08-02 16:46

Babies as young as four months have taste in fine art, study shows
Our taste in fine art can develop from a very early age, researchers have said, after they found babies as young as four months can demonstrate artistic preferences. When shown landscapes by the Dutch post-impressionist painter Vincent van Gogh, psychologists at the University of Sussex found both babies and adults mostly favoured the same paintings, with Green Corn Stalks (1888) proving to be the most popular. The team at the university’s Sussex Baby Lab also uncovered that infants liked paintings that had more edges – such as those featuring leaves or branches – and curved lines. In their findings, published in the Journal of Vision, the researchers said aspects of artistic preferences may be hardwired from an early age. Our study also appears to have identified features of adult aesthetics that can be traced back to sensory biases in infancy Philip McAdams Philip McAdams, a doctoral researcher at the University of Sussex and lead author on the paper, said: “It was fascinating to find that babies respond to the basic building blocks of the paintings, such as edges and colours, and that these properties could explain large amounts of why babies look at, and adults like, particular artworks. “Our study also appears to have identified features of adult aesthetics that can be traced back to sensory biases in infancy. “Our findings show that babies’ visual systems and visual preferences are more sophisticated than commonly thought.” For the study, which was in collaboration with children’s sensory brand, Etta Loves, the researchers recruited 25 babies, aged four to eight months, and 25 adults. The babies sat on their parent’s lap while 40 pairs of images, featuring landscape paintings by Van Gogh, were shown on a tablet. Adults were also shown the same paintings and asked which image in the pair they found to be more pleasant. Recordings showed babies looked longer at the Van Gogh landscapes that adults also rated as most pleasant. These paintings featured high colour and lightness contrasts as well as lots of the colour green. The most preferred Van Gogh painting was Green Corn Stalks whilst the least preferred was Olive Grove (1889). But researchers also found small differences in the artistic tastes between adults and babies. For example, they found that infants preferred paintings that contained the most edges and curved lines, which the adults did not seem to favour. Professor Anna Franklin, head of the Sussex Colour Group and founder of the Sussex Baby Lab, and lead author on the paper, said: “We’ve been amazed by how much the young babies responded to the art. “Although newborn babies’ vision is very blurry, our findings demonstrate that by four months old, babies can see well enough to look longer at some paintings than others, and can pay attention to many of the artistic details.”
2023-08-02 16:16

ADHD symptoms in children can be transformed with brain stimulation therapy
Stimulating the brain using electrodes could help ease symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children, a study has found. Transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) works by sending a mild electrical current to the brain through two electrodes on the scalp. The study, led by researchers from the University of Surrey and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem – and published in the Translational Psychiatry journal, explored the use of tRNS alongside cognitive training as a treatment for ADHD. Roi Cohen Kadosh, head of the School of Psychology and professor of cognitive neuroscience at the University of Surrey, said: “I believe that the scientific community is duty-bound to investigate and develop evermore effective and longer-lasting treatments for ADHD.” The clinical trial included 23 newly diagnosed and unmedicated children between the ages of six and 12, who were recruited from groups referred to the ADHD clinic by doctors, teachers, psychologists or parents. Researchers at the computerised neurotherapy lab at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem administered tRNS during cognitive training each weekday over a two-week period. The parents of 55% of the group reported “significant clinical improvement” in ADHD symptoms to researchers, compared to 17% in a control group that was given placebo brain simulation. Prof Kadosh said the findings demonstrate the treatment “has the potential to transform the lives of children and their families”. Future studies, with larger and more varied samples, should help establish this as a viable therapy for ADHD, and help us understand the underlying mechanisms of the disorder Dr Mor Nahum ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder and symptoms include hyperactivity, an inability to focus and impulsiveness. According to the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (Nice), it is present in about 5% of children globally. Researchers are now preparing to start a larger clinical trial using tRNS and cognitive training. “If successful, this approach will be approved as a medical device for ADHD by the United States Food and Drug Administration,” Prof Kadosh said. Dr Mor Nahum is co-lead of the study and head of the computerised neurotherapy lab at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. She added: “This is an important first step in offering new therapeutic options for ADHD. “Future studies, with larger and more varied samples, should help establish this as a viable therapy for ADHD, and help us understand the underlying mechanisms of the disorder.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Black LGBTQ+ icons everyone should know Ashley James: ‘We have a totally warped idea of what a mum should be’ Host Maya Jama’s glamorous Love Island outfits cost over £10,000
2023-08-02 15:51

RIP Republic Wireless: Dish Wireless Moves Subscribers to Boost Infinite
Republic Wireless, once one of the wireless industry’s quirkier experiments in business models, is now
2023-08-02 06:24

Starbucks Revenue Misses Estimates as Its US Growth Slips
Starbucks Corp.’s quarterly sales fell short of analysts’ estimates, a sign that momentum may be slowing for the
2023-08-02 04:16
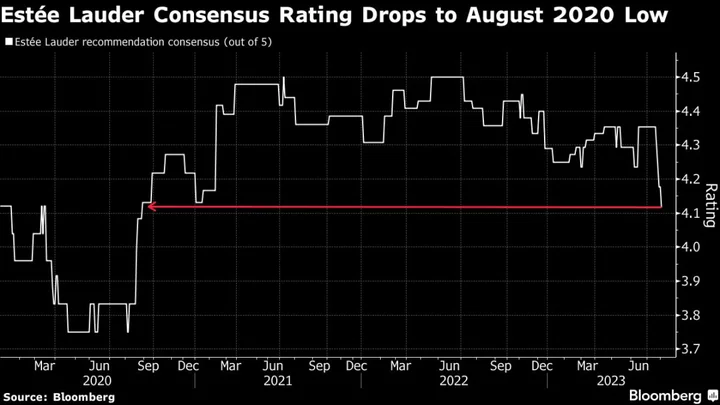
Estée Lauder Bulls Flee, Citing China Recovery Concerns
A slew of Wall Street analysts have downgraded Estée Lauder Cos. ahead of the beauty company’s quarterly earnings
2023-08-02 04:16

US Halts Allegiant-Viva Aerobus Partnership on Mexico Rift
Regulators in the US suspended the review of a joint venture between ultra low-cost carriers Allegiant Travel Co.
2023-08-02 02:50
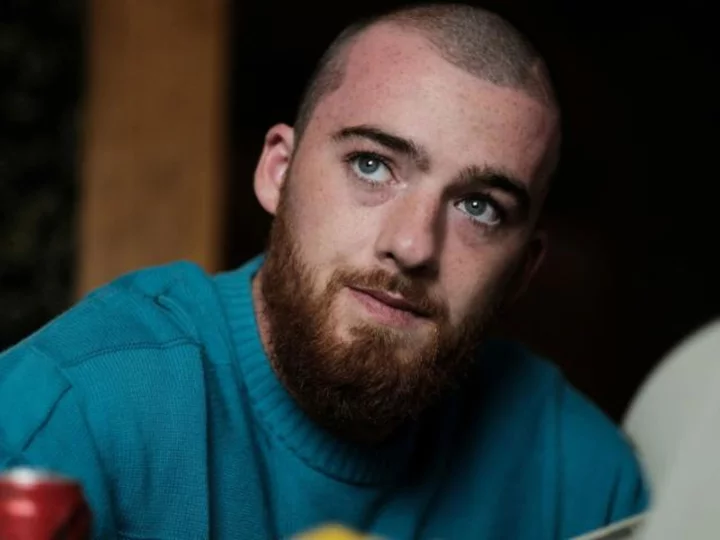

Angus Cloud's unlikely journey from waiter to celebrated actor
There's a viral video of actor Angus Cloud that almost went unnoticed.
2023-08-02 00:57

Lenovo Reportedly Working on Its Own Steam Deck Rival
It looks like Lenovo is preparing its own competitor to Valve's Steam Deck. The company
2023-08-02 00:52

Honkai: Star Rail Review
With Honkai: Star Rail, developer Hoyoverse takes a stab at a space opera, and the
2023-08-01 23:50

YouTube Is Letting AI Write Video Summaries
YouTube is experimenting with allowing an AI to generate summaries for videos. As Android Police
2023-08-01 22:17
