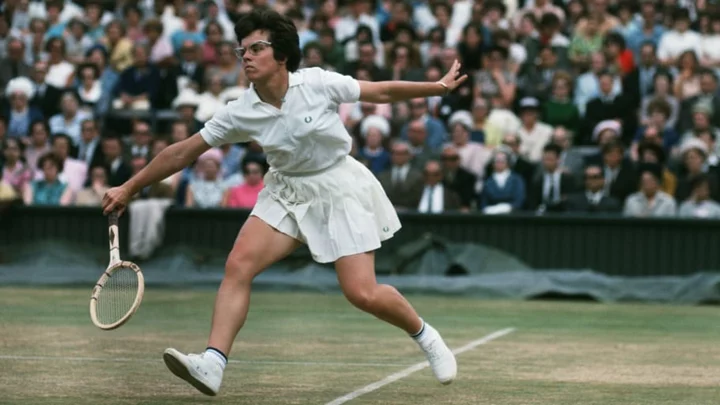

11 Facts About Billie Jean King
Billie Jean King is one of tennis’ most celebrated athletes. But she also championed gender equality efforts and fought for equal pay in sports.
2023-06-01 20:21
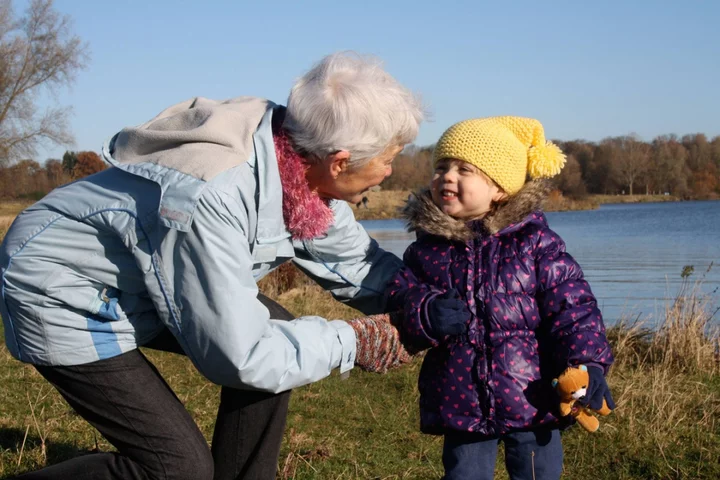

10 ways to explain dementia to children
Dementia is very hard for adults to understand – so imagine how perplexing it must be for a child. Not only does a close family member like their grandma or grandpa start forgetting things, but dementia – the most common form of which is Alzheimer’s – can mean those affected have problems with planning, decision-making and language, as well as changes in their mood and behaviour. And they’re only going to get worse. But how do you explain all this to a child? “Finding out someone close to you has dementia is difficult for everyone, and we all need time to adjust and come to terms with our feelings,” says Dr Tim Beanland, head of knowledge management at the Alzheimer’s Society. “Children and young people are no different, but it can be harder for them, as they may not properly understand what dementia is, or they might find it harder to cope with their feelings. “One of the most important approaches is to listen to the concerns of the young person or child. It’s very important to try to get a sense for how much they can cope with, and tailor the discussion accordingly.” Here are Beanland’s suggestions for how to explain dementia to a child… 1. Explain what dementia is Make sure you know the facts about dementia, and convey at least some of what you know to your child, in an age-appropriate manner. “Explain as clearly and calmly as possible, at a level that the child can understand,” advises Beanland. “Try to get a sense of how much detail they can cope with.” 2. Be clear and honest Try to be as honest as you can, offering clear explanations and plenty of reassurance, Beanland says. “It’s important to make sure they know they can ask questions any time they need to.” 3. Acknowledge the affected person’s behaviour Talk about the behaviour of the person with dementia, for example if they’re forgetting where they are, or not recognising family members, says Beanland. Make sure your child knows you understand the behaviour may seem strange to them. 4. Listen carefully to what children have to say Try to imagine the situation from your child’s point of view, suggests Beanland. “Think about their relationship with the person with dementia – this will help you find out if they’re worrying about something specific,” he says. 5. Be patient You may need to repeat your explanations on different occasions, depending on the age and level of understanding of the child. 6. Tell the school If your child is at school, it’s often a good idea to let staff know that your relative has dementia, says Beanland. That way, if the child’s behaviour is affected at all by what’s happening with their relative, teachers may realise what’s triggering the behaviour. 7. Remind children you’re still there for them It’s important to reassure children that others are still there for them, says Beanland. “They need to know that, despite all the pressures, they are still loved – however preoccupied or frustrated other people may be sometimes.” He says this can help to provide opportunities for them to talk about any concerns they might have. “Give the child plenty of reassurance and hugs, and don’t be afraid to use humour, if it feels appropriate,” Beanland says. “It can help if you can laugh together.” 8. Get the person with dementia to talk to the child about their diagnosis if possible If the person with dementia has received an early diagnosis, or has a form of dementia that doesn’t initially affect their understanding and communication, they may be able to talk about their diagnosis to a child themselves. “This can potentially be a good way of reducing fear and maintaining a positive relationship,” says Beanland. 9. Let them know you are there Encourage the child to ask any questions they have, and let them know they can always talk to you without being judged. “You could also set aside a regular time to talk or do activities together when they can speak with you alone,” suggests Beanland. 10. Talk about living well with dementia Once you’ve explained as well as you can what dementia is and what’s happening to your loved one, try to be positive about their remaining abilities. “Focus on the things that the person with dementia can still do, as well as those that are becoming more difficult,” Beanland suggests. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live How to make your home summer ready Jetting off this summer? Doctors share essential in-flight health tips How do heterosexual celebrities become LGBTQ+ icons?
2023-06-01 15:49

13 Big Changes We Want in MacOS 14
Apple will almost certainly announce the next version of macOS at its annual Worldwide Developers
2023-06-01 02:48
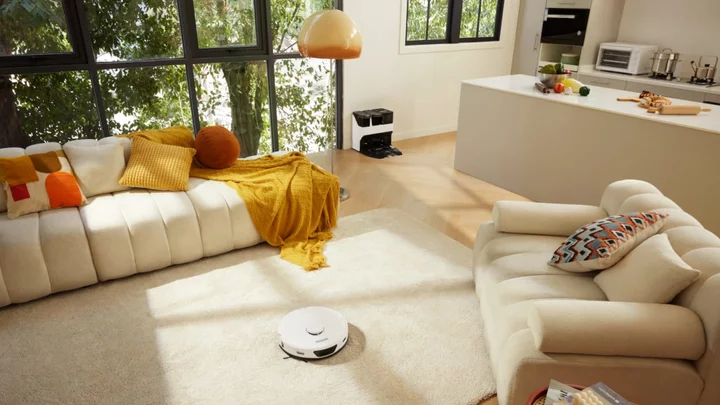

6 Simple Ways to Keep Your House Spotless Without Compromising Cleanliness
Mental Floss and Roborock have teamed up to share six simple tips for keeping your house clean without compromising cleanliness.
2023-05-31 22:45

10 Explorers Who Vanished Without a Trace
From a record-breaking mountain climber to a British adventurer who may have died searching for a city that doesn’t exist and beyond, these explorers have fates that are shrouded in mystery.
2023-05-30 00:18

Liz Weston: 5 ways to simplify and reduce your money clutter
Streamline how you manage your money to save yourself time and reduce stress
2023-05-29 20:27

20 easy pranks that are actually really good
To be clear, many pranks are mean, and even more of them are a waste
2023-05-29 11:57
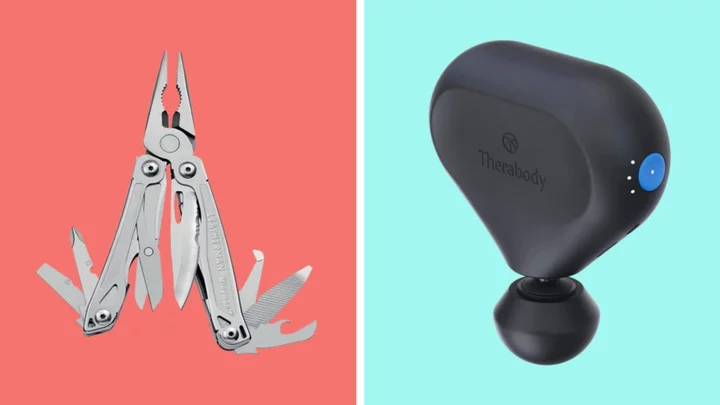
15 Great Father’s Day Gifts to Celebrate Every Kind of Dad
Have a dad who is hard to shop for? Here are the best Father’s Day gifts for all kinds of father figures, including everything from multitools to beard-trimming kits and more.
2023-05-27 03:56
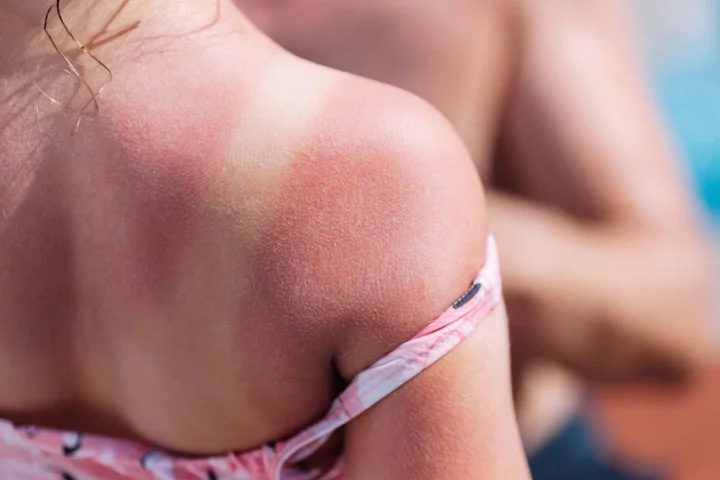

Bank holiday heatwaves predicted: 6 sunburn myths that could put you at risk
After a largely disappointing spring, the bank holiday weekend is set to bring with it the warmest weather of the year so far. Temperatures are predicted to go as high as 24C on Saturday and Sunday, according to the Met Office, with dry and sunny weather expected to last into next week. Many of us will be heading out to enjoy the sunshine – but as ever, it’s important to protect your skin from harmful UV rays. When it comes to tanning and sunburn, there are a variety of misconceptions that still abound, and the consequences of not following sun protection advice can be severe – especially as skin cancer rates across the UK have been rising, charities have warned. Here are five sunburn myths that could be putting your health at risk… 1. The UK and Irish sun isn’t strong enough for sunburn We might grumble about the gloomy weather in our part of the world, but the risk of sunburn remains for a large part of the year. “The sun can be strong enough in the UK between mid-March and mid-October to burn you,” says Karis Betts, senior health information manager at Cancer Research UK, which is working in partnership with Nivea Sun to educate consumers on how to be sun safe. “You’re most likely to get burnt in the middle of the day, when the sun is at its highest point, not necessarily its hottest.” UV rays are generally strongest between 11am and 3pm, she says: “It’s wise to take a break in the shade or indoors during these hours. And remember, you can burn through clouds.” 2. You have to go red before you go brown Our complexion can turn darker in the sun due to the release of melanin as the skin attempts to protect itself, but that doesn’t mean you need to turn lobster-red first in order to try and get a tan. “This is one of the biggest myths in sun protection, and it contributes to skin damage and skin cancer cases,” says Abi Cleeve, MD of Ultrasun UK. “The fact is that as soon as the skin reddens, it’s in trauma. A ‘trauma tan’ occurs from inadequate protection where the skin appears to tan more quickly, but hasn’t – it has burned. This only ensures that the skin peels, leaving the skin tan-less in days.” To avoid this pattern, Cleeve recommends gradually building up your time in the sun, and using higher SPF sunblock: “Use high UVA and UVB filter SPF – a minimum of SPF30 with a UVA filter over 90% will protect the skin and still tan, just more slowly [and] minimising long-term damage and peeling.” 3. The odd sunburn doesn’t make a difference It’s easy to get caught out by a sudden blast of sunshine, but don’t be fooled into thinking that one instance of sunburn here and there doesn’t matter. “This is something I hear a lot but unfortunately, it’s just not true,” says Betts. “Damage to our skin from the sun is the number one cause of melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, and skin damage from the sun builds up over time – it doesn’t go away after the burn fades.” That’s why wearing sunblock is crucial – even more so for children. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation: “Even one blistering sunburn in childhood or adolescence more than doubles your chances of developing melanoma later in life”. 4. People with darker skin don’t get sunburnt “Anyone can get sunburnt – including people with darker skin – but your risk of getting sunburnt and how sunburn feels will depend on your skin type,” says Beth Vincent, health information manager at Cancer Research UK. “For people with lighter skin tones, sunburned skin is usually red, sore, and swollen. In people with darker skin tones, sunburned skin might not change colour but will often feel irritated, itchy, tender and sore.” While people with lighter skin tones are generally at higher risk of sunburn and skin cancer, you should still use sunblock if you’ve got darker skin or a tan. In terms of sunscreen for darker skin tones, Betts recommends: “At least SPF15 and four or five stars [for UVA protection]. Make sure to reapply it regularly and generously, especially after swimming, sweating or towelling.” 5. All body parts are created equal when it comes to sunscreen “Burning – overexposure to UVB rays – tends to happen where the skin is closer to the bone structure, and especially where the part of the body faces directly the sun’s rays,” says Cleeve. “Tops of feet, shoulders, décolleté, top of the scalp and the nose – take extra care in these areas.” Other easy-to-miss areas include the scalp or parting, ears, areas around swimwear such as straps, and shorts that might move or rise up through the day. Cleeves top tip for all-over protection? “Do your sun cream naked! Then any movement in straps, shorts won’t suddenly bare unprotected skin to the sun’s rays.” 6. Aftersun products repair the damage done by sunburn “No, they don’t,” says Vincent. “While aftersun products may soothe the unpleasant symptoms of sunburn, they won’t fix any damage that was done to the DNA inside your cells.” If you do start to notice signs of burning, cover up or get out of the sun as soon as possible, she warns: “Don’t spend more time in the sun that day – even with sunscreen. And don’t rely on aftersun to fix the damage, because it can’t.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Dame Esther Rantzen faces stage four lung cancer: key facts about the disease Camilla receives ‘beautiful’ compliment after meeting children at historic library 7 foods that could help you get better sleep
2023-05-26 19:57
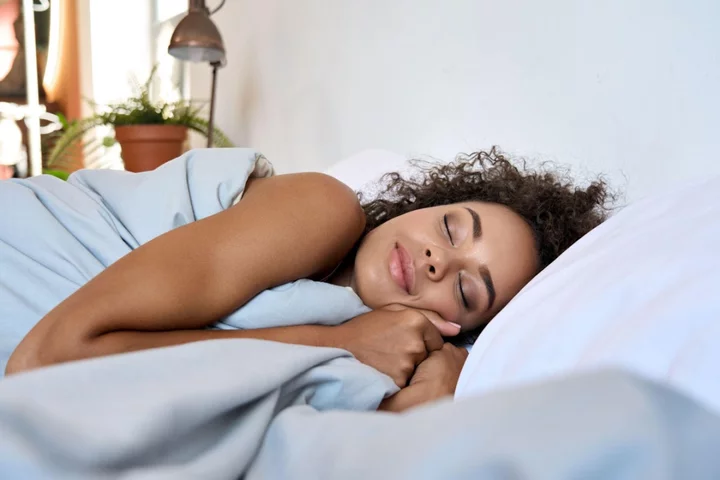

7 foods that could help you get better sleep
Wondering whether certain foods can affect your sleep patterns – or if eating certain things could actually help improve your sleep? The relationship between diet, sleep and overall health is two-sided, says Gabi Zaromskyte, registered nutritionist and founder of Honestly Nutrition. “Meaning what we eat and drink affects our sleep, but also, the quality and duration of sleep can affect our food choices,” Zaromskyte explains. “Scientific research has increasingly shed light on the significant impact of dietary choices on cognitive function, mood, and overall physical and mental health,” she adds. Certain dietary patterns and specific nutrients have been found to influence the sleep-wake cycle, sleep latency (the time it takes to fall asleep), and sleep architecture (the different stages of sleep), notes Zaromskyte. She continues: “And the quality and timing of our food and beverage intake can impact the production of sleep-regulating hormones, such as melatonin, which plays a critical role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle.” However, as Dr Maja Schaedel, co-founder of The Good Sleep Clinic points out, it’s important to understand that most research done so far shows that even though certain foods may be higher in melatonin, that does not necessary equate to falling asleep quicker. “You may have higher levels of melatonin, but if you’ve got stuck in a bad habit of tossing and turning for two hours before drifting off, or waking at 3am and not being able to return to sleep, foods high in melatonin are not going to solve your problem,” says Schaedel. She suggests that generally, it’s best to eat your evening meal at least two hours before bed, to avoid any indigestion, spikes in blood sugar and increase in body temperature that can occur while digesting. “If you tend to get peckish later in the evening, then plan a snack an hour or two before bed,” Schaedel adds. “It’s best to have something high in protein, like Greek yoghurt or nuts, and low in complex carbohydrates to avoid any spikes and falls in blood sugar.” Also, it might be wise to avoid the usual culprits which can trigger discomfort. “Fatty and spicy foods can cause heartburn and indigestion which can hinder good sleep, as well as alcohol, caffeine and tobacco,” says Lisa Artis, deputy CEO of The Sleep Charity. Here, experts share their go-to foods for supporting healthy sleep… 1. Cheese “Cheese gets a bad reputation as it’s commonly believed to give us nightmares, but actually it’s the opposite,” says Artis. “Cheese, and other dairy products, contain tryptophan, an amino acid which helps us to nod off more easily, and calcium which helps to reduce stress.” 2. Cherries To find out if foods with naturally occurring melatonin make a difference for you, Artis suggests giving cherries a go – particularly tart cherries, which have been found to naturally boost the production of melatonin. Zaromskyte says several studies have shown significant improvements in sleep quality and duration when consuming Montmorency cherries or tart cherry juice, where the concentration of naturally occurring melatonin and phytochemicals is higher compared to whole cherries. 3. Low sugar cereals “Cereal can also help us to sleep – but we must be mindful of the type of cereal,” says Artis. “There are lots of sugary options on the market, so try to avoid these.” She says complex carbohydrate-rich foods increase the availability of tryptophan in the bloodstream which, in turn, may help us to nod off. 4. Bananas Bananas are an excellent source of magnesium, potassium and tryptophan, says Artis. In other words, a great choice when it comes to supporting sleep. “While bananas have lots of great qualities for sleep, all fruit contains sugar too, so be mindful of this in the run up to bedtime,” she notes. “Try blending one banana with one cup of milk or soya milk to make an ideal evening drink.” 5. Almonds “Almonds are a brilliant source of calcium and magnesium, which promotes both sleep and muscle relaxation,” says Artis. “Magnesium also helps to regulate melatonin levels and keep blood sugar levels stable overnight.” 6. Magnesium rich foods Magnesium, an essential mineral, has been found to play a crucial role in sleep regulation – and can influence sleep quality and duration, says Zaromskyte. “It acts as a co-factor in more than 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including those involved in the production and regulation of neurotransmitters and hormones that impact sleep.” Some magnesium-rich foods cited to help improve sleep quality include pumpkin seeds, spinach, almonds and dark chocolate (which is packed with health-enhancing antioxidants too). 7. Omega-3 rich foods Although research is limited, some evidence suggests foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids may promote better, longer sleep, says Zaromskyte. “For example, walnuts are a source of melatonin and other sleep-regulating compounds, such as an amino acid tryptophan and omega-3 fatty acids,” she says. “Other omega-3-rich foods include oily fish, like salmon, trout, mackerel and sardines, chia seeds and flaxseeds.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Household energy bills set to fall from July: 7 ways to help keep bills as low as possible Queen of Rock ‘n’ Roll Tina Turner’s most iconic looks 11 stylish ways to kit out kids’ bedrooms
2023-05-26 15:24

'Yellowjackets': 10 burning questions we have for Season 3
We made it through the wilderness of Yellowjackets Season 2 — and just like at
2023-05-26 13:20

Tears of the Kingdom: 10 Tips to Get You Started on Your Next Zelda Adventure
The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild is a perfect video game, so how
2023-05-26 03:58
