
Another Threshold candle recall? Target recalls 2.2 million products over burn and laceration risks
It’s time to check your candle supply again
2023-08-11 00:53
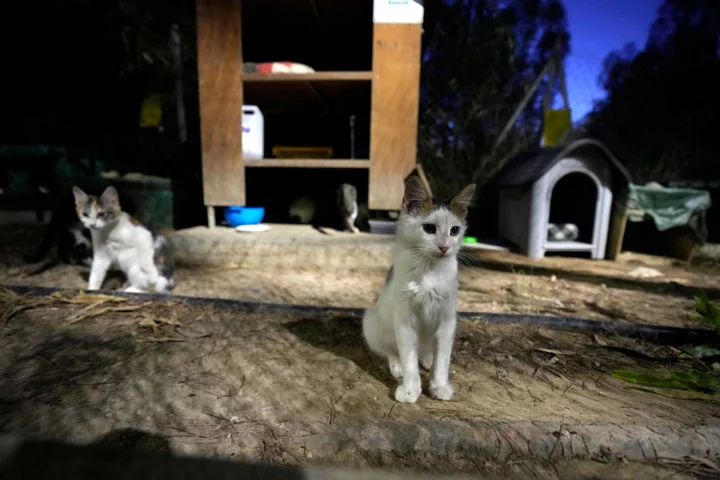

Cats given anti-Covid pills for humans after thousands die from feline virus in Cyprus
Cats in Cyprus are being treated with anti-Covid pills meant for humans after a feline virus killed thousands of animals on the island. An estimated 8,000 cats have died from Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP), prompting the government to approve the use of stockpiled human coronavirus medication. The disease is almost always lethal if left untreated, but medication is effective in around 85 per cent of cases. However, the high price of the medication made it inaccessible to vets and pet owners in Cyprus, activists said. The government’s veterinary services director, Christodoulos Pipis said the first batch of 2,000 medication packages will be used to mitigate what has been called the “FCov-2023” outbreak, with a total of 80,000 pills becoming available later. Mr Pipis told the Guardian the health ministry rolled out the treatment on 8 August, celebrated as International Cat Day. Each pill will cost €2.5 (£2.16) and can be bought at local vets’ offices, after a formal examination and diagnosis. It is hoped the move will end the outbreak, first noticed in the Cypriot capital of Nicosia in January. FIP, which spreads through contact with cat faeces, has spread across the island four months later, the Pancyprian Veterinary Association said. Local animal activists claimed FIP has killed 300,000 cats, but PVA president Nektaria Ioannou Arsenoglou called that figure an exaggeration. The disease is unrelated to Covid-19 and cannot be contracted by human beings. However, the active ingredient in anti-Covid medication Lagevrio, molnupiravir, has proven effective in treating cats who’ve contracted FIP. The feline virus has been around since 1963, Ms Arsenoglou added, but previous epidemics in the UK, US, Taiwan, and Greece remained confined to catteries and eventually fizzled out without the use of any medication. However, the outbreak in Cyprus has also affected indoor cats. Read More Maui wildfires – live: Devastating wildfire burns historic town ‘to the ground’ in Hawaii and kills 36 Wildfire devastates Hawaii's historic Lahaina Town, a former capital of the kingdom A feline virus mutation in Cyprus caused far fewer cat deaths than claimed, veterinary leader says UK man bitten by cat contracts previously unknown and ‘extensive’ bacterial infection Ukraine war live: Putin ‘considers coming face to face with world leaders’ at G20 Poland to double troops number at border with Belarus
2023-08-10 23:25

6 tips for cutting costs on back-to-school shopping
An estimated $135 billion will be spent on back-to-school and back-to-college shopping in 2023, according to the National Retail Federation, representing the second-largest spending period of the year, behind only the holidays
2023-08-10 22:27

Big fashion is getting bigger. Parent of Coach will buy Versace owner Capri in $8.5 billion deal
Tapestry, parent company of luxury handbag and accessories retailer Coach, is buying the owner of fashion brands including Michael Kors, Versace and Jimmy Choo, Capri Holdings
2023-08-10 19:56
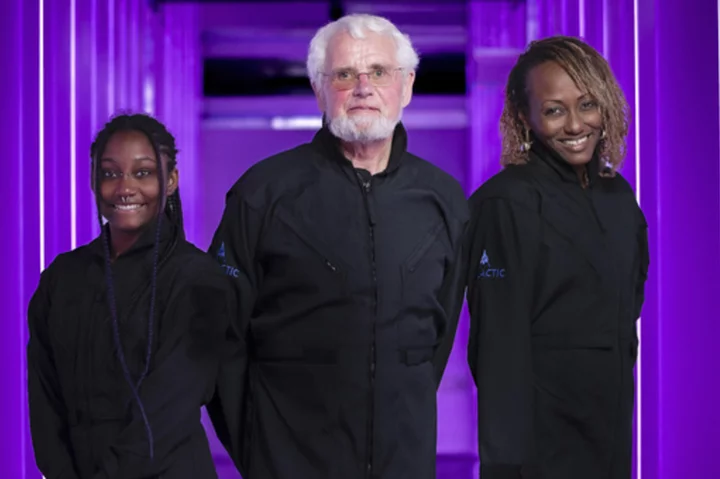

Virgin Galactic all set to fly its first tourists to the edge of space
Virgin Galactic is finally taking its first space tourists on a rocket ship ride after years of delays
2023-08-10 19:23
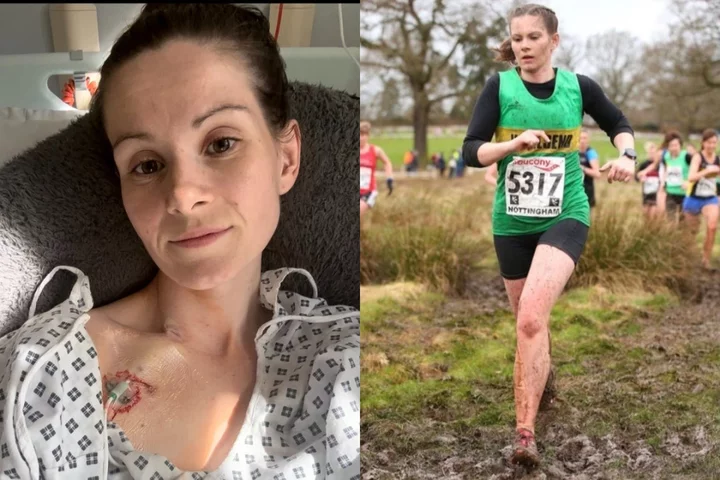

‘Long Covid has taken away my ability to eat food or urinate - I don’t recognise myself anymore’
A young woman whose health “deteriorated rapidly” after being diagnosed with long Covid and suffering a liver bleed is now in a wheelchair, feeds herself through a tube in her chest and has been unable to urinate in three years. Abigail Snowball, 29, was told she suffered from a rare condition known as Fowler’s Syndrome a few months after she was diagnosed with long Covid in July 2020 and her bladder stopped working. The social worker, from Northumberland, says she was “never sick” and enjoyed long runs before testing positive for coronavirus in early 2020 and feeling a sharp pain under her ribs which scans showed was a bleed on her liver. Abigail had not fully recovered from the virus and since the diagnosis, her health has gone from bad to worse, to the point where she has not been able to urinate in three years. She now depends on her husband Mark, 34, to carry her to the bathroom so she can empty her bladder, which can take up to four hours, and has not been able to enjoy a mouthful of food for nearly a year. “I had never really been ill before,” Abigail told PA Real Life. “As a child, I was always really lucky and never poorly. I look back at pictures from before Covid and I don’t even recognise myself.” Abigail had completed a 20-mile race, the Run Northumberland BIG 20, just a week before testing positive for Covid and having to quarantine away from Mark, who works in maintenance for Nissan. “It was very much at the start of the pandemic, back at the time when there weren’t any vaccines or much testing,” she said. “It was just tiredness like I’ve never felt before in my entire life. I remember having a cup of tea and struggling to lift the mug up.” Like many other people’s experience of catching Covid, Abigail’s health improved over the next 10 days. “I did get better, but I never fully recovered,” she said. But a couple of months later, while visiting her parents, Jane and Ray Cresswell, in Cornwall on holiday, she suddenly began feeling a sharp pain under her ribs. “It was a really strange location to have pain,” she added. She visited the GP a week later and was admitted to Northumbria Specialist Emergency Care Hospital (NSECH) in July 2020, where scans revealed Abigail had suffered a bleed on her liver. “That’s when they diagnosed me with long Covid,” she said. “There was no other explanation, because they tested for blood disorders and carried out a scan. “They asked me if I had a fall or accident, but there was literally nothing.” Abigail was recovering from her liver bleed in hospital late one evening when a nurse asked when the last time she urinated was. “I actually thought, ‘god, it wasn’t since this morning’,” she said. “From that point, my bladder never regained any function. That was really the start of my health declining quickly.” Doctors hoped her bladder block was simply a result of the liver “trauma” and that she would be on the mend soon. But, sadly, this was not the case. A few months later, Abigail was diagnosed with a rare condition called Fowler’s Syndrome, which causes women to have problems passing urine. Abigail’s condition has deteriorated over the past few weeks and she is now losing weight rapidly. “I am now sleeping on the sofa downstairs and my husband Mark is having to carry me to the toilet and back again,” she said. “We can spend up to four hours at a time trying to drain my bladder, and the pain is just unbearable. “I went from running 20 miles to using a wheelchair. You don’t realise how inaccessible the world is until you are in that position.” Since the diagnosis, Abigail has spent more than 350 days in hospital and undergone 12 surgeries, including one in October 2021 to try and reconstruct her bladder. To make matters worse, she developed intestinal failure last year, which means she can no longer eat food. “I haven’t eaten anything in a year now,” she said. Instead, she is fed through TPN (total parenteral nutrition), a tube in her chest which delivers nutrients directly into the blood stream. Abigail and Mark, who married earlier this year in May, both received close to six months of training on how to perform the feeding procedure given there is a high risk of infection. “We had never even heard of that – being fed through a line into your heart,” she said. Abigail has been told by doctors that her liver bleed was “extremely likely” to have been caused by Covid. While Covid is known to harm the lungs, it has also been found to affect other organs, including the heart, liver and kidneys, but wider research is needed to better understand its long-term effects. Liver problems are common among patients with Covid-19, according to a study carried out by researchers at Oxford University and published in the peer-reviewed journal Hepatology Communications. Abigail, whose condition is considered “severe”, is hoping to receive specialist treatment in London, known as bladder Botox, which involves injecting Botox into the bladder every three to nine months, but there is no guarantee this will work. “Because of how severe and complex my case is, we’ve exhausted all our options here and the doctors are saying that I need to see the specialists in London,” she said. “Removing my bladder completely remains on the cards, but it’s incredibly high risk because of my intestinal problems. “There is no cure for Fowler’s, so it’s about managing it in the best way possible.” The combination of health conditions has left Abigail unable to perform everyday tasks. “It’s funny because the things I want to be able to do are so normal,” she said. “Just being able to wake up, take the dog for a walk and go to work. “Things that in the past, I completely took for granted.” To help cover the costs, Abigail’s friend Emma Holt has set up a GoFundMe which has received thousands of pounds in donations. “We never imagined in our wildest dreams that we would raise the amount of money that we have already,” she said. “It’s the one thing that really keeps us going, when things are really difficult. “Knowing that we have so many people behind us and supporting us is amazing.” Fowler’s Syndrome is most often caused by infection or following surgery or trauma, but a link to long Covid has yet to be established and more research is needed. Dani Coombe, CEO, Fowler’s Syndrome UK said: “It’s too early to say if long Covid is a trigger for Fowler’s syndrome; we haven’t seen an increase in Fowler’s and retention post-Covid yet, and there is no indicator that urinary retention gets worse. “Our research into what patients believe triggered their urinary retention shows that infection is the most common trigger at 57 per cent, followed by surgery in 32 per cent of patients and trauma at 19 per cent. “It would be noteworthy to see in coming years if there is an increase in women with Fowler’s because of the trauma of Covid-19.” Read More Fake meat is dying, but that shouldn’t mean the end of veganism What I gained (and lost) from walking 10,000 steps a day for five months Woman behind ‘not real’ plane tirade identified as marketing executive with $2m home Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live
2023-08-10 18:52
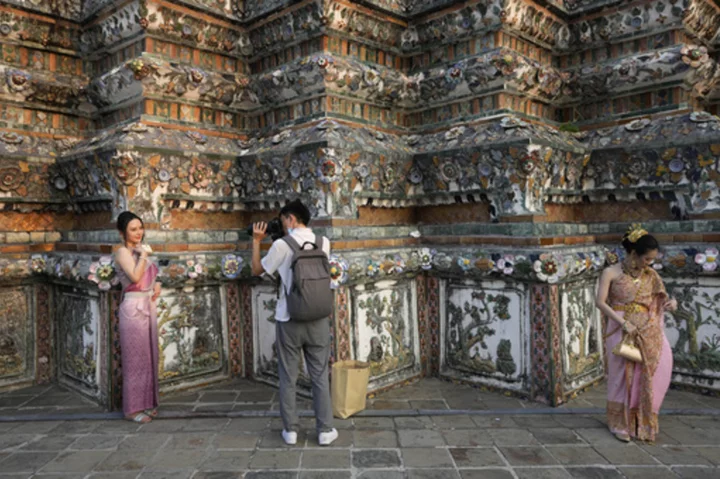

China expands the number of countries for travel by its big-spending tourists
China has increased the number of countries that its big-spending tourists can visit by more than 70 following the lifting of its last COVID-19 travel restrictions
2023-08-10 18:20
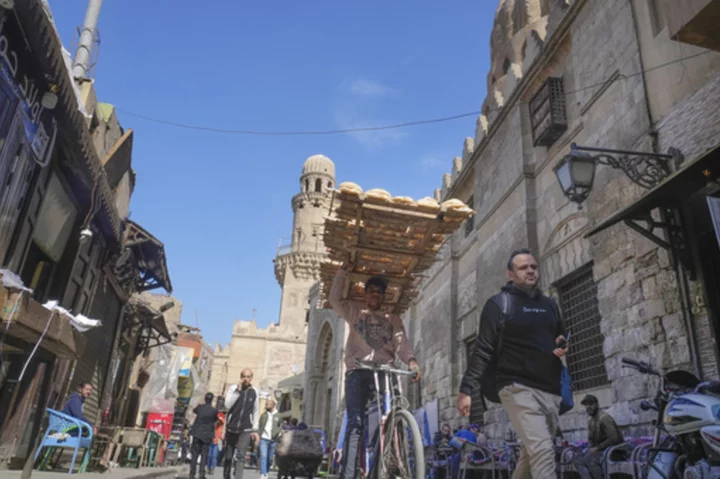

Egypt's inflation reaches record high of 38.2% in July, government data shows
Egypt’s national statistics bureau says inflation has reached a record high in July
2023-08-10 17:17
A year ago, an Iranian woman's death sparked hijab protests. Now businesses are a new battleground
Iranian authorities have for months done little to enforce the law on women wearing the mandatory headscarf, but now the country’s theocracy is pushing to make businesses the new battleground over the hijab
2023-08-10 13:51

Paper exams, chatbot bans: Colleges seek to 'ChatGPT-proof' assignments
ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence chatbots have become the go-to source for cheating in college
2023-08-10 12:19
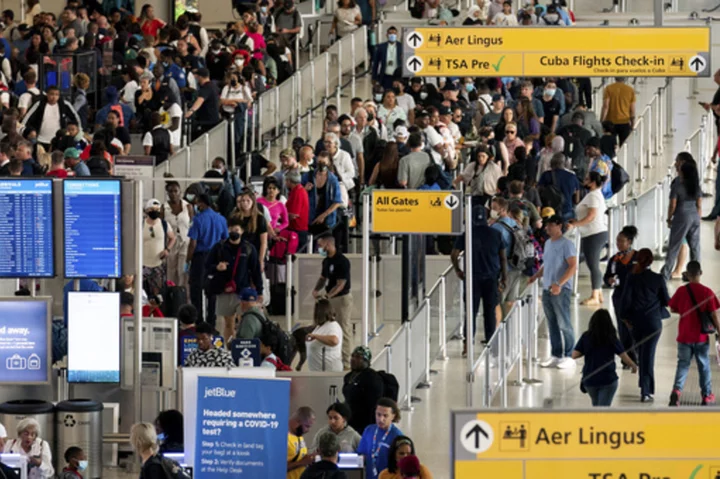

The FAA, lacking enough air traffic controllers, will extend limits on New York City-area flights
The Federal Aviation Administration is letting airlines continue to reduce their flights in the New York City area beyond summer and into this fall
2023-08-10 04:51
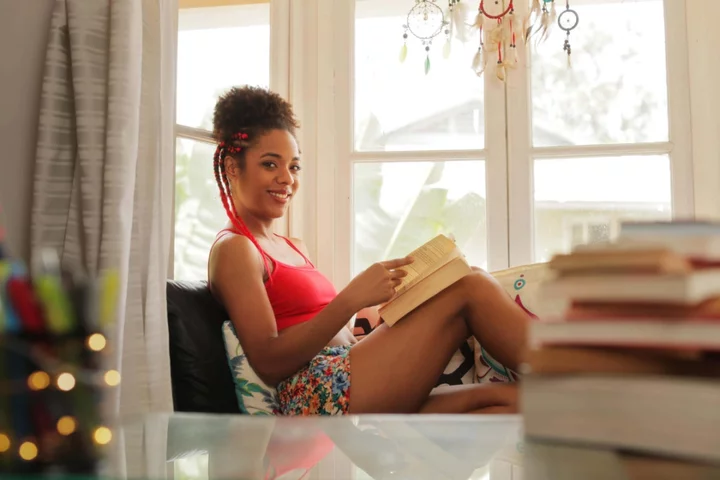

What is TikTok’s ‘soft life era’ and could it be the secret to happiness?
The term ‘soft life’ is trending on TikTok, with the #softlifeera tag clocking 12.2million views. While not brand new, it seems a growing number of social media users are leaning towards the lifestyle concept – but what does soft life actually mean and how can it benefit people? Where does the trend come from? As the wording suggests, soft life is all about veering away from stress and struggle and embracing a more easy and enriched life. But this isn’t just about life looking ‘perfect’ on social media. “Soft life isn’t new, however I’m really grateful to see its resurgence,” said Chlöe Pierre, founder of wellness platform thy.self and author of Take Care: The Black Women’s Guide To Wellness. “Essentially to me, especially as a black woman, soft life is about making choices that can avoid me having to live a much longer, and unsustainable, life in hardship. For me it’s about wellness in general, and sustainable wellness. “My only concern when seeing trends [on social media] is that they are inclusive, and generally they aren’t. First and foremost, soft life is a choice – and it’s a privilege to be able to make that choice,” Pierre added. “Originally, the soft life kind of movement had origins in places like Nigeria and other places around the continent, but was popularised via America and a lot of African American women, [who were often] fictional characters on TV. Because there weren’t, especially not in the UK, reachable or visible representations of black women and women of colour that had amassed a wealth, and therefore the privilege of living a ‘soft life’.”Permission to live a soft life For Dr Evelyn Okpanachi, author of The Emotionally Empowered Woman, it makes sense people are increasingly leaning towards the trend. “Collectively, we are still tired. We have had the Covid era, austerity and more, and we simply want to live and breathe a little. This is why we are leaning towards it more right now. Collectively, we are breathing a sigh of relief,” said Okpanachi. “Most people associate the soft life with booking last-minute flights, mojitos on the beach, dining at nice restaurants and all of the externalities. It is in part, but it a lot deeper than that. “Soft life is living life on your terms. Creating a career you want, the business you want, and looking after yourself holistically. This starts with empowering yourself to succeed by elevating your mindset and knowing you deserve to live a soft life.” Nothing comes easy Okpanachi noted the work that can be involved, however. “In order to enter the soft life era, the average person tends to go through an element of stress. Nothing comes easy,” she explained. “It is essentially about purposely creating a lifestyle with minimal stress and setting boundaries – boundary setting is key. It’s embracing the things that serve you and letting go/eliminating the things that don’t. We all deserve to live a soft life, and we all should. But we have to put the work in to attain it.” This is something social media can often miss out. As Pierre noted, influencers or celebrities may “show you one side of their life – you don’t get to see the struggle they have had to get to that point, or to maintain that lifestyle they have in front of the camera”. Making space for a softer lifeFor many, the dilemma is making these things a reality when work takes up so much energy, along with caring/parenting duties, health challenges and everything else. Pierre discusses in her book about how our identities can be “very wrapped up” in work, which can make it so much more draining – especially for black women who have faced “more hardship in the workplace, compared to other demographics”. Setting “clear expectations and intentions” for yourself can be helpful, she added, and getting to know yourself better. “So making clear expectations about who I am, what I will accept, and what I want – and having the belief that I don’t have to go through too much hardship, that it’s not a benchmark for who I am,” Pierre explained. “This can even be applied to dating.” Ditch the guilt Donna Noble, yoga teacher and author of Teaching Body Positive Yoga: A Guide To Inclusivity, Language And Props, also believes making things intentional is key for how people can embrace the soft life in their everyday routines. “[People] can prioritise their me-time and be intentional about it – for instance, meditating, journaling or doing yoga as soon as they get up (before the rest of the world invades their space), as this will set you up nicely for the rest of the day,” said Noble. “I believe rest and self-care are part of our birth-right – no feeling guilty for just being and not doing. Normalise taking the pause, and that it can be the most powerful thing we do in our day.” For those who struggle to put themselves first, Noble suggested taking time to work on giving yourself permission. “The key here is a shift in perspective and empowerment – you’ve got to discover the precious gem that is your wellbeing. Society’s old scripts may try to hold us back, but rewriting the narrative is where the magic happens,” she said. “Giving ourselves a permission slip to prioritise self-care isn’t just a luxury; it’s a necessity. It’s about understanding that nurturing ourselves isn’t selfish; it’s the foundation for health and wellbeing.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Kim Kardashian teased as the face of a major fashion brand Shoppers make seven big impulse buys per year on average – survey Even 4,000 steps a day could ‘reduce risk of death’ – study
2023-08-09 22:26
