
First-of-its-kind study finds laughter is indeed good medicine, especially for the heart
A new, first-of-its kind study has demonstrated that laughter can indeed be good medicine – especially for those with heart disease. Laughter therapy can increase the functional capacity of the cardiovascular system that includes the heart, lungs, arteries and veins, found the yet-to-be peer-reviewed research presented at the annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology in Amsterdam. Researchers, including Marco Saffi from the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre in Brazil, found reduced inflammation and better signs of health among coronary artery disease patients who engaged in a course of laughter therapy. They found laughter therapy sessions could cause the tissue inside a patient’s heart to expand, potentially leading to increased oxygen flow through the body. Until now, different treatments without the use of drugs have been studied in coronary artery disease patients, but the benefits of rehabilitation using laughter therapy was not fully assessed, scientists said. In the new study, the impact of laughter therapy on the functional capacity, tissue function as well as markers of inflammation in the bodies of patients with coronary artery disease was evaluated. The condition, which is one of the most common diseases in the world, arises when the heart’s coronary arteries struggle to supply the organ with enough blood, oxygen and nutrients. Scientists conducted a clinical trial involving 26 adults with an average age of 64 from August 2016 to December 2020, measuring each of their oxygen uptake and the widening of their main artery when blood flow increases. Researchers also measured levels of molecules in the patients’ bodies, indicative of inflammation such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM) and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM). Thirteen of the patients were assigned to the group that underwent laughter therapy by watching two self-selected TV comedy shows per week. The other 13 served as the control group and watched “neutral documentaries”, scientists noted. They said the study is the first controlled clinical trial to evaluate the impact of rehabilitation using laughter therapy on patients with coronary artery disease. It revealed an increase in the body’s peak oxygen uptake and improvements in tissue function as well as the body’s markers of inflammation. The new findings are in line with previous research that suggested having a good laughter session makes the body release endorphins, which are hormones that reduce stress and inflammation and help the heart and blood vessels relax. Based on the new results, presented at the world’s largest heart conference, scientists say laughter therapy may constitute an “effective form of cardiac rehabilitation in this patient population”. Read More How many steps a day can cut risk of early death (and it’s not 10,000) A broad genetic test saved one newborn's life. Research suggests it could help millions of others Snoring before age 50 is a health ‘red flag’, experts suggest How many steps a day can cut risk of early death (and it’s not 10,000) Experts warn that snoring before you turn 50 is a health ‘red flag’ ‘Boy moms’ called out for dubious logic behind teaching their sons to cook
2023-08-28 13:56
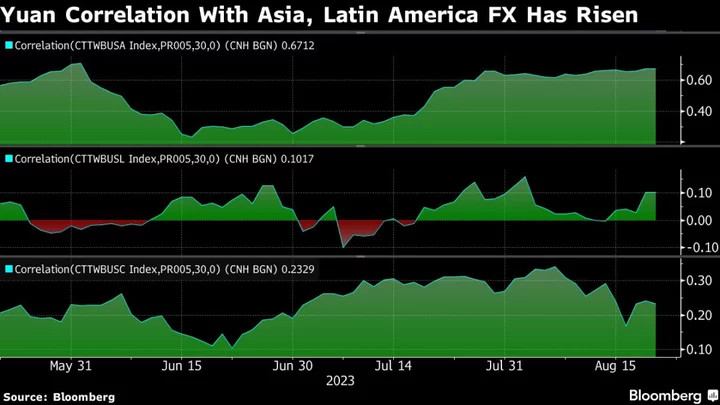
China’s Worsening Economic Slowdown Is Rippling Across the Globe
China’s economy was meant to drive a third of global economic growth this year, so its dramatic slowdown
2023-08-28 05:58

Alicia Witt chronicles how she overcame breast cancer and the tragic death of her parents with her music
Alicia Witt, singer and actor known for roles in "Urban Legend" and "Mr. Holland's Opus," tragically lost both of her parents when they were found dead in their home in December 2021.
2023-08-28 00:25
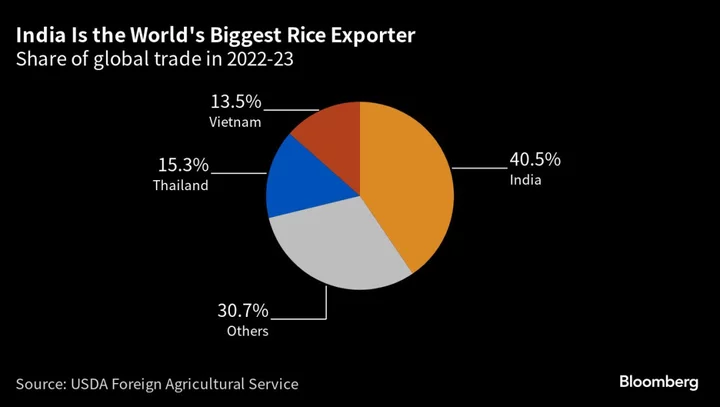
India Further Tightens Rice Shipments in Threat to Global Supply
India, the world’s biggest exporter of rice, imposed more curbs on shipments of the grain in a move
2023-08-27 22:47
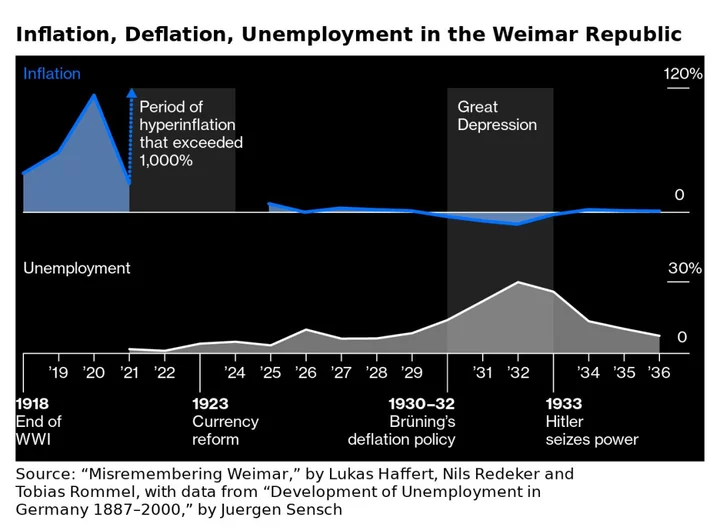
German Inflation Trauma of 1923 Strikes an Uneasy Chord Today
By late-1923, hyperinflation had rendered Germany’s currency so worthless that one woman used several billion marks of banknotes
2023-08-27 13:47
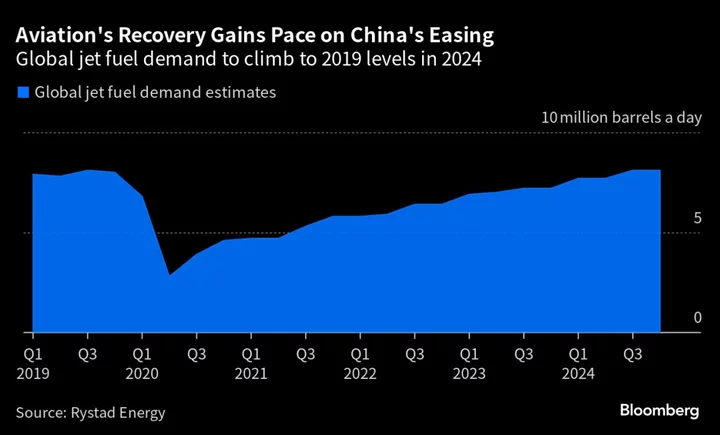
China’s Travel Rebound Risks Super-Charging Jet Fuel Prices
After years of pent-up demand for leisure and business travel due to the ravages of Covid-19, millions of
2023-08-27 08:50
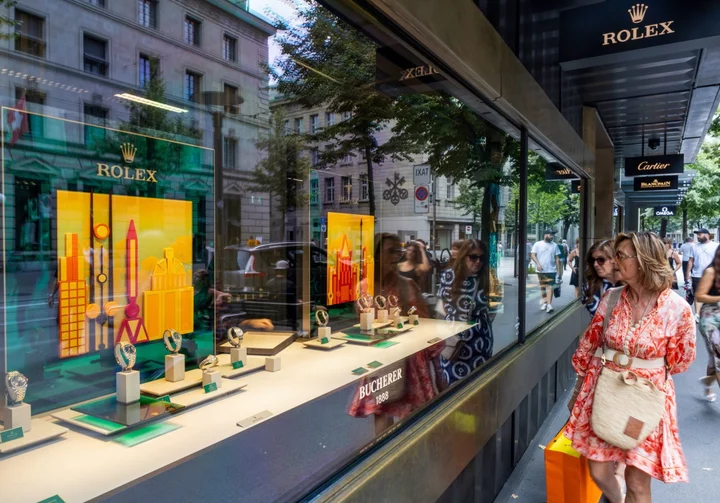

Century-Old Swiss Watch Dynasty Ends With Scion Selling to Rolex
Over more than a century, three generations of Bucherers built one of the most exclusive watch and jewelry
2023-08-26 19:23
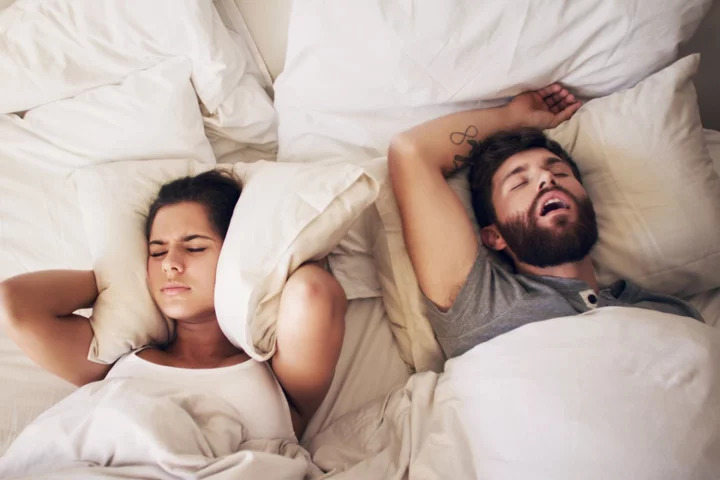

Snoring before age 50 is a health ‘red flag’, experts suggest
Young adults who snore at night have a significantly higher risk of having a stroke and developing heart disease when they get older, a study has warned. Doctors have said that snoring should be treated as a “red flag” among adults below the age of 50. The study found that young adults who snore are 60 per cent more likely to develop a stroke when they reach middle age, and five times more likely to develop a heart rhythm disorder. The researchers presented their findings at the European Society of Cardiology Congress in Amsterdam. They examined data from 766,000 US adults aged 20 to 50. These included 7,500 adults with obstructive sleep apnoea, a condition that causes interruptions to normal breathing during sleep. This can lead to loud snoring and interrupted sleep as sufferers wake up while struggling to breathe. The study found that, over the 10-year follow-up period, patients with sleep apnoea were 60 per cent more likely to suffer a stroke compared to those who did not snore as frequently. They were also five times more likely to develop atrial fibrillation, a heart condition that causes irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate. Symptoms of atrial fibrillation include heart palpitations, dizziness and shortness of breath. Lead author Professor Sanjiv Narayan, of Stanford University, said: “Sleep apnoea is really common but we sort of ignore it because we think it’s trivial or just a little bit of a nuisance. “Until now no one’s really shown the magnitude of the size of the risk for heart diseases. That’s what really surprised us.” He added that the study looked at “relatively young people” who may not know they are at risk. “If they had a stroke, it would devastate young families. It could take them away from their workplace. It would destroy their lives for the next 40 years.” The researchers suggest that GPs should ask patients regularly if they snore and highlight if as a heart health “red flag” that could show they need more tests or medication. Obstructive sleep apnoea is fairly common and is estimated to affect 1.5m adults in the UK. However, according to the British Lung Foundation, up to 85 per cent of sufferers are undiagnosed and go untreated. Men who are elderly and overweight are particularly prone to sleep apnoea. Interruptions to normal breathing can cause a dip in blood oxygen and cause the heart and blood vessels to strain. Prof Narayan explained: “When you are unable to breathe it raises the pressure in the lungs until you ultimately wake up gasping for breath. That puts a pressure load on the heart, which causes stretch in the heart chambers, and that could cause the atrial fibrillation. “Another theory could be that the oxygen levels in the blood fall for tens of seconds and that could put stress on the heart.” Sleep apnoea can be treated using a CPAP machine, a device that pumps air into a mask that the patient wears over their mouth or nose while they sleep. The NHS also recommends making lifestyle changes such as losing weight if the patient is overweight and exercising regularly, which can improve symptoms. Sleeping on your side may also help relieve sleep apnoea. Read More I feel it in my fingers: Why more of us should start eating with our hands Sean O’Malley sparks outrage after claiming it’s OK if he cheats on his wife Woman praised for refusing to switch seats with child during eight hour flight Liam Payne reveals he was hospitalised due to a ‘serious kidney infection’ ‘Boy moms’ receive backlash for teaching sons how to cook - but for the wrong reason This is how stress affects different parts of the body
2023-08-26 17:49

Climate Change Is Helping Pests and Diseases Destroy Our Food
Pests and diseases are exacerbating crop shortages that have sent prices for goods like cocoa, olive oil and
2023-08-26 16:52
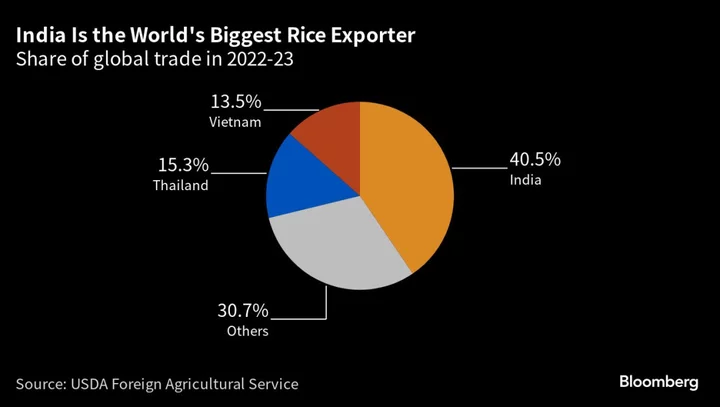
India Tightens Rice Exports in Threat to Global Food Prices
India imposed more curbs on shipments of rice to ensure its food security, a move by the top
2023-08-26 14:18
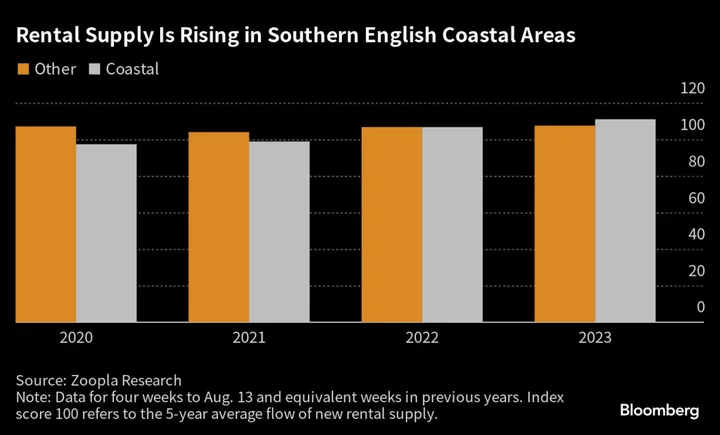
The Sun Sets on Holiday Let Investors as UK Staycation Boom Ends
For the aspirational middle classes, it seemed a no brainer: buy property in one of Britain’s holiday hot-spots
2023-08-26 13:51

Instacart’s IPO Plans Show Bottom-Line Benefit of Strategy Shift
Instacart is preparing to go public as its core grocery-delivery business is slowing and it pivots to a
2023-08-26 09:52
