
Iceland Ireland owner placed into examinership
Last week the firm was ordered to withdraw all imported frozen food of animal origin.
2023-06-21 02:48

The College World Series Jello Shot Contest's Integrity Has Been Compromised
The infamous College World Series Jello shot contest record should be questioned.
2023-06-21 00:47

Ransomware Gang To Reddit: We Stole 80GB Of Your Data
It turns out the hack Reddit suffered back in February may have resulted in a
2023-06-20 23:45

How to Work the `Quiet Luxury’ Trend Into Your Office Attire
While the concept of “quiet luxury” may be the subject of think pieces and sharply rising Google searches,
2023-06-20 22:57

What are the symptoms of laryngitis and how long does it take to recover?
Getting a case of laryngitis is an unpleasant experience and can happen to anyone. But singers are more prone to the throat condition and the latest performer to have come down with laryngitis is Arctic Monkeys frontman Alex Turner. The band were forced to cancel a concert in Dublin that was scheduled for Thursday (22 June), and their appearance at Glastonbury this weekend has also been thrown into doubt. In a statement, the Arctic Monkeys said: “Alex is suffering from acute laryngitis and, following medical advice, has been ordered to rest.” According to the NHS, the illness can sometimes come on suddenly, but can be linked to other illnesses, such as colds and flu. It occurs when the voice box or vocal cords in the throat become irritated or swollen. It’s an uncomfortable illness, but can usually be treated at home or with help from a pharmacist. Here’s everything you need to know about laryngitis. What are the symptoms? Laryngitis can sometimes come on without warning and patients feel the worst during the first three days. The main symptoms are a hoarse voice or sometimes losing your voice; an irritating cough that doesn’t go away; always needing to clear your throat; and having a sore throat. In children, there can be additional symptoms including a temperature of 38C or above; losing their appetite; or having difficulty breathing, but this last symptom is rare. How long does it take to treat? Most people recover from laryngitis after one to two weeks, and don’t need to see a GP. The NHS advises treating the condition by drinking plenty of fluids and gargling with warm salty water, if you are an adult. You should also try to rest your voice as much as possible. This means speaking as little as you can, and if you must, do not talk loudly or whisper as both can strain your voice. Keeping the air moist is also helpful in treating laryngitis. You can increase the amount of moisture in the air by putting out bowls of water. Be aware that central heating and air conditioning can make the air drier. Staying out of smoky or dusty places will also help, as well as avoiding smoking cigarettes. You should steer clear of caffeine or alcohol as they can cause dehydration. Pharmacists can help with treating the symptoms by providing paracetamol or ibuprofen, cough syrup, gargling solution, or lozenges to soothe the throat. When should I see a GP about laryngitis? You should see your GP if your symptoms do not improve after two weeks, or if you keep getting laryngitis or problems with your voice. The GP may carry out some procedures to try and figure out what is the cause, including looking inside the throat with a small mirror, wiping a cotton bud around the back of the throat to be tested, and arranging a blood test. You may also be referred to an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist if the condition keeps occurring. If it is very painful or you are finding if difficult to swallow, you should call 111. If you or your child are having difficulty breathing, you should call 999 or go to A&E. Read More I couldn’t climax, so I let ‘big testosterone’ take me for a ride ‘What in the wingardium leviosa?’: Emma Watson shocks fans with ‘levitating’ dress Harry and Meghan ‘Duke and Duchess of Dior’ rumours untrue, report says What is egg freezing and how does it work? Regular napping could be good for brain health, research suggests Dramatic rise in the number of women freezing their eggs
2023-06-20 21:29

Spotify Plans New Premium Tier, Expected to Include HiFi Audio
Spotify Technology SA is planning a more expensive subscription option that’s expected to include high-fidelity audio in an
2023-06-20 20:47

What is egg freezing and how does it work?
New figures show a dramatic rise in the number of women deciding to freeze their eggs. A report from the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HEFA) found that egg and embryo freezing are now the fastest growing fertility treatments in the UK. Egg freezing and storage saw a 64% rise between 2019 and 2021 – increasing from 2,576 cycles to 4,215 completed. What is egg freezing? It’s where a woman’s eggs are extracted and frozen immediately for fertilisation at a later date. Gynaecologist Dr Larisa Corda said it’s a “means of helping preserve fertility for the future”. Freezing the eggs at the point of extraction means they avoid the decline in quality that’s associated with ageing. “It essentially means that a woman becomes her own egg donor later in life, when she decides she wishes to have children,” she said. What’s the process? “It involves the same sort of procedure as the first part of IVF, where a woman takes injections to stimulate her ovaries, to encourage follicles to grow and lead to egg maturation over several days. “After that, the eggs are collected via a simple surgical technique using a needle placed into the vagina and then into the ovaries, to aspirate the eggs which are there,” Corda said. The daily injections (usually for eight to 11 days) involved in the first part of the process is to encourage the ovaries to produce more eggs. “They may be uncomfortable and lead to side-effects like bloating, abdominal pain, nausea, headaches and other hormonal symptoms, such as breast soreness and changes to your mood,” she added. Women are usually put to sleep for the egg retrieval, during which, a long needle is inserted into the vagina to reach the ovaries and remove the fluid in each follicle that contains an egg. “This is all done under direct ultrasound guidance and normally takes around 30 minutes. You will not feel anything during the procedure, but afterwards, you may have some cramps and a bit of bleeding, which all normally settles down within 24-48 hours.” How many eggs are usually frozen each time? It really depends how many are produced by the patient at the time. Corda said the number of eggs doesn’t give a good indication on the quality though – which is only revealed after the eggs are fertilised to create embryos further down the line, when the woman or couple want to try to have a baby. “Because of this reason, women are advised to freeze between 10-15 eggs, to give themselves a good, reasonable chance. This may involve doing several rounds of egg freezing, but there’s no guarantee of success,” she said. The aim varies depending on the clinic though, and the “numbers needed when older become much more unpredictable, and it also becomes much harder to get a good number of eggs too”. What’s the success rate? The success rates are dependant on age and the quality of the eggs. “Not surprisingly, the highest live birth rates from previously frozen eggs are shown to come from women who undergo the procedure before they are 30,” she noted. “However, the average age at which women freeze their eggs is around 37, with many women closer to 40 by the time they consider doing this.” She said it’s generally agreed that the best time is before age 36, when most women’s eggs are still a sufficient quality and you’re more likely to use them in the future (as opposed to someone age 25 and more likely to fall pregnant without medical assistance). It’s important to know that some eggs won’t actually make it, even if they were fine at the freezing stage. Dr Suvir Venkataraman, from the Harley Street Fertility Clinic, added: “For a good prognosis patient, i.e. under 35 with no known fertility issues, roughly 90% of eggs survive freezing and thawing by vitrification. “Approximately 70% of those will be fertilised by good sperm to create embryos. Approximately 50% of those embryos will develop well. And there’s approximately 30% chance of live birth per embryo transferred.” How much does it cost? The Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) estimate the average cost of freezing eggs is £7,000-£8,000 – including medication, storage costs and the later process of thawing and transferring to the womb. But it varies from clinic to clinic. What else should you consider? Arm yourself with all the facts on the costs, and understand it’s not a guaranteed insurance policy for getting pregnant in the future. “It’s important to see a fertility specialist to get assessed before considering egg freezing, as the decline in egg number and quality can start much earlier for some women,” Corda said. “If you’re not sure what clinic to go to, the HFEA website has lots of great and useful information to help you to decide and check out their credentials. “Egg freezing does not offer any guarantees, but for a lot of women, it is the best possible chance of having their own biological children later in life.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live How can you save money on your wedding food? Regular napping could be good for brain health, research suggests Dramatic rise in the number of women freezing their eggs
2023-06-20 18:49

Malaysia Nears Southeast Asia’s First Nationwide Airbnb Control
Malaysia is inching closer to becoming the first country in Southeast Asia to impose widespread curbs on short-stay
2023-06-20 18:25

Wild Weather in China Poses New Threat to Country’s Grain Crops
China is bracing for more extreme weather in coming days, bringing further risks to grain production across the
2023-06-20 17:48
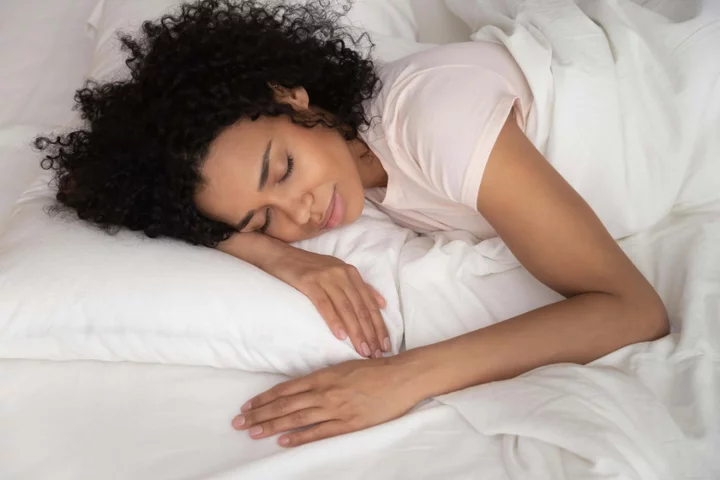

Regular napping could be good for brain health, research suggests
Regular daytime naps could be good for brain health, new research suggests. Daytime napping could slow the rate at which brains shrink as we age, the study led by researchers at UCL and the University of the Republic in Uruguay found. The researchers hope their findings into the health benefits of sleeping during the day will reduce any stigma that still exists around daytime napping. The study suggests the average difference in brain volume between people programmed to be habitual nappers and those who were not was equivalent to 2.6 to 6.5 years of ageing. Our findings suggest that, for some people, short daytime naps may be a part of the puzzle that could help preserve the health of the brain as we get older Dr Victoria Garfield, UCL Senior author Dr Victoria Garfield, MRC Unit for Lifelong Health & Ageing at UCL, said: “Our findings suggest that, for some people, short daytime naps may be a part of the puzzle that could help preserve the health of the brain as we get older.” The study, published in the journal Sleep Health, analysed data from people aged 40 to 69. Past research has suggested people who have had a short nap perform better in cognitive tests in the hours afterwards than those who did not nap. The new study looked at whether there was a causal relationship between daytime napping and brain health. Researchers looked at 97 snippets of DNA thought to determine people’s likelihood of habitual napping. They compared measures of brain health and cognition of people who are more genetically programmed to nap with people who did not have these changes in DNA, using data from 378,932 people from the UK Biobank study. They found that, overall, people predetermined to nap had a larger total brain volume. The genetic variants – DNA changes – influencing the likelihood of someone to nap were identified in an earlier study looking at data from 452,633 UK Biobank participants. But the researchers did not find a difference in how well those programmed to be habitual nappers performed on three other measures of brain health and cognitive function. Lead author and PhD candidate Valentina Paz, University of the Republic (Uruguay) and MRC Unit for Lifelong Health & Ageing at UCL, said: “This is the first study to attempt to untangle the causal relationship between habitual daytime napping and cognitive and structural brain outcomes. “By looking at genes set at birth, Mendelian randomisation avoids confounding factors occurring throughout life that may influence associations between napping and health outcomes. “Our study points to a causal link between habitual napping and larger total brain volume.” Garfield added: “I hope studies such as this one showing the health benefits of short naps can help to reduce any stigma that still exists around daytime napping.” Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Dramatic rise in the number of women freezing their eggs 9 glorious gardens to visit this summer How to keep flying insects out of your home
2023-06-20 16:50

Dramatic rise in the number of women freezing their eggs
There has been a dramatic rise in the number of women freezing their eggs in the UK, while more single people are now opting for IVF, new figures show. A report from the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HEFA) found that more people than ever before are undergoing procedures, with egg and embryo freezing now the fastest growing fertility treatments in the UK. Egg freezing and storage increased from 2,576 cycles in 2019 to 4,215 in 2021 (a 64% rise), while embryo storage also rose. Some experts have said the Covid-19 pandemic had a big impact on the numbers of women wanting to freeze their eggs in the hope of preserving their fertility. Restrictions on socialising may have prompted some women to think more about their fertile window, and decide to try to increase their reproductive choices Sarah Norcross, Progress Educational Trust Sarah Norcross, director of the Progress Educational Trust, said of the latest data: “The dramatic rise in the number of egg freezing cycles could be linked to the pandemic. “Restrictions on socialising may have prompted some women to think more about their fertile window, and decide to try to increase their reproductive choices.” The HFEA data also shows there was a 10% rise in IVF and donor insemination cycles between 2019 and 2021 (around 7,000 more cycles). Meanwhile, the average age at which women have fertility treatment with IVF has risen – to 36. This compares to an average age of almost 31 for women who conceive naturally. The regulator’s report shows that patients in heterosexual relationships accounted for around 90% of all IVF patients in 2021. Meanwhile, the number of IVF patients in female same-sex relationships increased from 1,649 in 2019 to 2,201 in 2021 (a 33% rise) and single parents rose from 2,001 in 2019 to 2,888 in 2021 (a 44% rise). This means that single patients and patients in female same-sex relationships had the biggest increase in IVF use from 2019 to 2021. When it comes to success in getting pregnant using own eggs, the average overall IVF pregnancy rate using fresh embryos increased from 10% per embryo transferred in 1991 to 29% in 2021. Patients aged 18 to 34 had the highest pregnancy rate per embryo transferred at 41% in 2021. Meanwhile, pregnancy rates per embryo transferred increased from 8% in 1991 to 33% for patients aged 35 to 37, and was 25% for patients aged 38 to 39 in 2021. For patients aged 40 to 42, the pregnancy rate per embryo transferred increased from 6% in 1991 to 16% in 2021. Our report shows that the average age of IVF patients has increased to 36, around five years older than mothers who get pregnant naturally and these aftershocks could mean that the average age of an IVF patient continues to rise Julia Chain, HFEA For patients aged 43 to 50, the pregnancy rate per embryo transferred increased from 1% in 1991 to 6% in 2021. Live birth rates per embryo transferred have increased from 7% in 1991 to 25% in 2021 for patients aged 35 to 37 and from 6% in 1991 to 17% in 2021 for patients aged 38 to 39. For those aged 40 to 42, the live birth rate per embryo stands at 10%, but plummets for women aged 43 and over. Meanwhile, the average IVF pregnancy rate using frozen embryo transfers has increased from around 7% in the 1990s to 36% in 2021. The average IVF birth rate using frozen embryo transfers also increased from around 6% in the 1990s to 27% in 2021. Julia Chain, chairwoman of the HFEA, said: “Overall, the new HFEA report paints a promising picture. It shows treatment numbers are back at pre-pandemic levels and thanks to improved clinical and laboratory practice, over time pregnancy rates are increasing. “Despite the pandemic being declared officially over, the aftershocks are still being felt as delays across other areas of healthcare prevent some patients accessing fertility services. “Our report shows that the average age of IVF patients has increased to 36, around five years older than mothers who get pregnant naturally and these aftershocks could mean that the average age of an IVF patient continues to rise. “Although pregnancy rates have increased, the likelihood of success decreases with age. “For some patients, this may mean they never get the baby they hoped for and that’s heartbreaking.” More patients than ever before are paying privately for IVF. The number of IVF cycles funded by the NHS continued to vary across the UK with an overall 16% decrease to 20,000 cycles in 2021 from around 24,000 in 2019.
2023-06-20 16:49
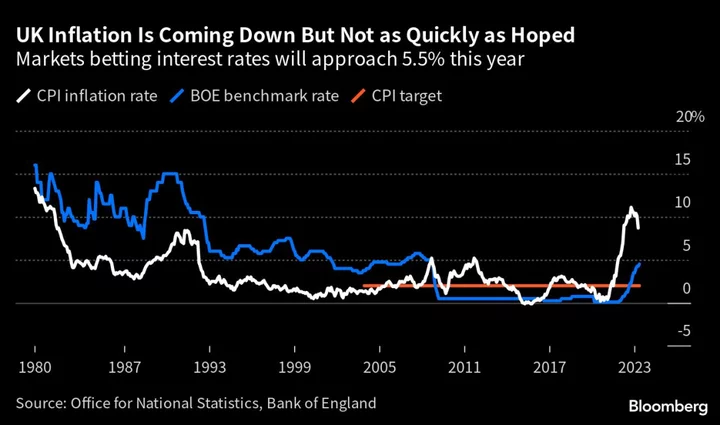
UK Food Price Inflation Shows Signs of Easing in Two Surveys
UK food price inflation may have passed its peak, with two separate surveys showing an improvement. The market
2023-06-20 16:18
