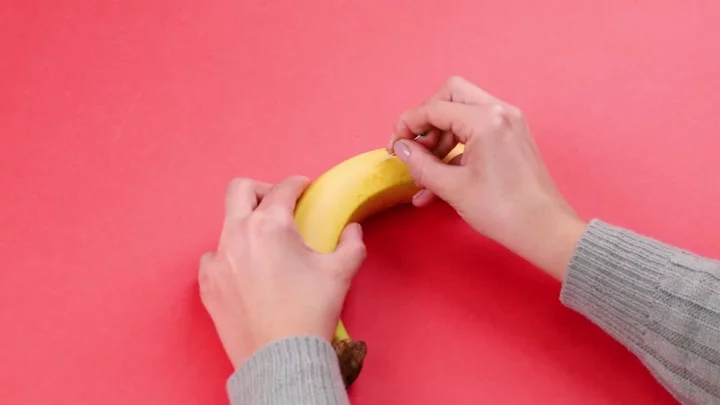

The black bit at the end of a banana is not as gross as you might think
When you chow down on a banana, you might often see a black bit at the end and it looks a bit gross. But what is it? Some people think it is the seed, but these are found down the middle, if at all, as the Cavendish variety of bananas, which is commonly sold typically doesn’t produce any seeds. It is actually something completely different. Bananas are technically berries and the black bit is the nub of the flower from which the giant banana berry grew. Bananas grow on trees in bunches, and the end is actually the top of the fruit while the hard stalk is the bottom. But given most people eat bananas by snapping off the stalk first, the residual flower nub is left at the end. This black bit is entirely edible but people often throw it away because it has a tough texture and a bitter taste. So now you know, there is nothing stopping you from getting one of your five a day. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-14 20:24
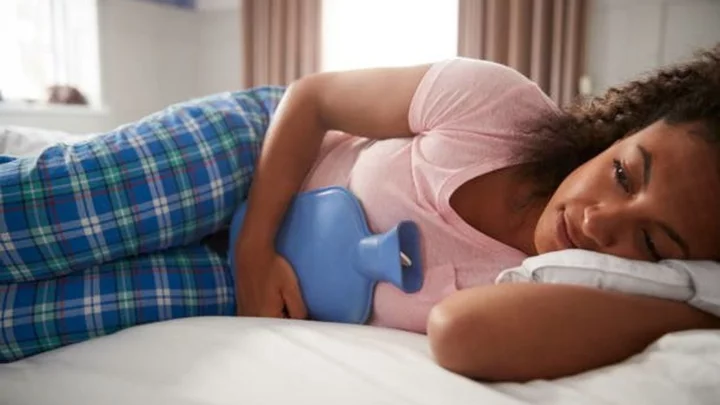

Study discovers vast numbers of women experience mental health issues because of period pain
A study has shown that millions of women and girls experience debilitating periods, that even cause mental health problems. A survey of 3,000 women and girls in the UK aged 16 to 40 for the Wellbeing of Women charity found that 86 per cent had had mental health problems, such as depression, anxiety and mood changes, in relation to their period, Meanwhile, of those surveyed, 96 per cent had experienced period pain, with 59 per cent saying their pain was severe. 91 per cent had experienced heavy periods, with 49 per cent saying their bleeding was severe. Even though these are common symptoms in women and girls with gynaecological conditions such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, fibroids and polycystic ovary syndrome, the report found that 51 per cent of respondents felt their healthcare professional had failed to take their problems seriously, and 82 per cent said they needed better access to accurate information on period problems. A further one-third never seek medical help, and more than half say their symptoms are not taken seriously, despite other symptoms including pain, heavy bleeding and irregular cycles. Prof Dame Lesley Regan, the chair of Wellbeing of Women, said: “It’s simply unacceptable that anyone is expected to suffer with period symptoms that disrupt their lives, including taking time off school, work, or their caring responsibilities, all of which may result in avoidable mental health problems. “Periods should not affect women’s lives in this way. If they do, it can be a sign of a gynaecological condition that requires attention and ongoing support – not dismissal.” Wellbeing of Women has launched its “Just a Period” campaign, which Regan said aims to address “the many years of medical bias, neglect and stigma in women’s health”. This includes tips on how to get the most out of seeing your GP and what women should do if they feel they have been dismissed by health professionals. Responding to the findings, Dr Ranee Thakar, the president of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, said: “All too often women are living with debilitating symptoms, waiting to receive support or treatment for far longer than they should. “Access to high-quality information and support about periods, gynaecological conditions and their symptoms is vital to ensuring that women and girls get the help that they need at the right time.” Caroline Nokes, the Conservative MP and chair of the women and equalities committee, which is conducting an inquiry into reproductive and gynaecological health, said: “There is a terrible phrase: ‘Well, it’s just a period, why are you making a fuss about that? Can’t you just get on with it?’ Yet many women and girls are experiencing horrendous period symptoms and gynaecological conditions. Endometriosis alone affects 1.5 million women in the UK and costs the economy £8.2bn. Now is the time for change.” Anneliese Dodds, the shadow secretary of state for women and equalities, said: “Over the past few years, we have opened up the conversation around the menopause, and now we need to see this change with periods as well.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-14 17:56
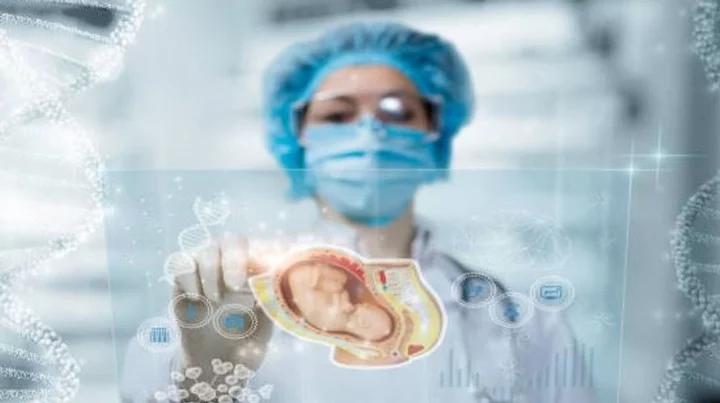
Human embryo created without using sperm or eggs
Scientists in Israel have created a model of a human embryo from stem cells, without using sperm, eggs or a womb. A team at Israel's Weizmann Institute of Science made the model, which resembles an embryo at day 14, when it acquires internal structures but before it lays down the foundations for body organs, and the work was published in the journal Nature. But the scientists involved said it would take a long time yet to create an embryo from scratch. Team leader Jacob Hanna said the team took stem cells derived from adult human skin cells, as well as others cultured in the lab, then reverted the cells to an early state.They then manipulated them to make a model of an embryo, rather than an actual or synthetic one. "The question is, when does an embryo model become considered an embryo? When that happens, we know the regulations. At the moment we are really, really far off from that point," Hanna said. However, they said the work could open the door to new ways to test the effect of drugs on pregnancies, better understand miscarriages and genetic diseases, and maybe grow transplant tissues and organs. "They are not identical. There are differences from human embryos, but still, this is the first time, if you open an atlas or a textbook, you can say - yeah I can really see the similarity between them," said Hanna. "In about 1 percent of the aggregates we can see that the cells start differentiating correctly, migrating and sorting themselves into the correct structure, and the farthest we could get is day 14 in human embryo development," he said. Their next goal, Hanna said, is to advance to day 21 and also reach a threshold of a 50 per cent success rate. Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz, a professor of development and stem cells at the University of Cambridge, said the study joins six other similar human embryo-like models published from teams around the world this year, including from her lab. "None of these models fully recapitulate natural human development but each adds to ways in which many aspects of human development can now be studied experimentally," she said. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-08 18:29
Scientists believe they have found a cure for alcoholism
Alcohol addiction ruins millions of lives every year, but scientists may have found a cure for this terrible affliction. A new treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) has been trialled in monkeys with impressive results and, if these translate to human trials, the impact could be monumental. A team of neuroscientists and physiologists from across the US tested a new type of gene therapy to see if they could directly target the underlying brain circuitry associated with sustained heavy drinking. As they noted, in the journal Nature Medicine, people suffering from AUD commonly return to alcohol use even if they attempt to quit. This is largely to do with what’s known as mesolimbic dopamine (DA) signalling – meaning how the central nervous system circuit communicates the feelgood neurotransmitter dopamine. A protein called glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is key to keeping these neurons in this reward circuitry functioning. However, experts have found that levels of GDNF are reduced in people with AUD during periods of alcohol abstinence, most notably in a region of the brain called the ventral tegmental area (VTA), as IFLScience notes. Therefore, the researchers decided to test whether using gene therapy to deliver more GDNF to the VTA could help reinforce this crucial dopaminergic signalling and prevent patients from suffering an alcoholic relapse. The team of scientists explained how alcohol consumption in non-addicts prompts the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable buzz feeling, but chronic alcohol use causes the brain to adapt and stop releasing so much dopamine. “So when people are addicted to alcohol, they don’t really feel more pleasure in drinking,” Dr Kathleen Grant, a senior co-author of the study, said in a statement. “It seems that they’re drinking more because they feel a need to maintain an intoxicated state.” For their research, Dr Grant and her colleagues used eight rhesus macaque monkeys, who were exposed to increasing concentrations of alcohol over four 30-day “induction” periods. The monkeys then had free access to alcohol and water for 21 hours a day for six months, during which they developed heavy drinking behaviours. This was then followed by a 12-week abstinence phase, with the GDNF treatment performed four weeks in for half of the subjects. The gene therapy was delivered using a a viral vector containing a copy of the human GDNF gene injected directly into the primate’s VTA, according to IFLScience. And the results were truly jaw-dropping. “Drinking went down to almost zero,” Dr Grant said. “For months on end, these animals would choose to drink water and just avoid drinking alcohol altogether. They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.” The most exciting aspect of their findings is the suggestion that gene therapy could offer a permanent solution for people with the most severe cases of AUD. This will be a welcome glimmer of hope to many, given that some 29.5 million people were diagnosed with AUD in the US alone in 2021, according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Of these 29.5 million sufferers, almost a million (894,000) were aged between 12 and 17. It’ll likely be some time before we know for sure whether the gene therapy can be rolled out in humans, but it’s an important first step in tackling this devastating disorder. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-01 20:57
Scientists may have just found a cure for alcoholism
Alcohol addiction ruins millions of lives every year, but scientists may have found a cure for this terrible affliction. A new treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) has been trialled in monkeys with impressive results and, if these translate to human trials, the impact could be monumental. A team of neuroscientists and physiologists from across the US tested a new type of gene therapy to see if they could directly target the underlying brain circuitry associated with sustained heavy drinking. As they noted, in the journal Nature Medicine, people suffering from AUD commonly return to alcohol use even if they attempt to quit. This is largely to do with what’s known as mesolimbic dopamine (DA) signalling – meaning how the central nervous system circuit communicates the feelgood neurotransmitter dopamine. A protein called glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is key to keeping these neurons in this reward circuitry functioning. However, experts have found that levels of GDNF are reduced in people with AUD during periods of alcohol abstinence, most notably in a region of the brain called the ventral tegmental area (VTA), as IFLScience notes. Therefore, the researchers decided to test whether using gene therapy to deliver more GDNF to the VTA could help reinforce this crucial dopaminergic signalling and prevent patients from suffering an alcoholic relapse. The team of scientists explained how alcohol consumption in non-addicts prompts the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable buzz feeling, but chronic alcohol use causes the brain to adapt and stop releasing so much dopamine. “So when people are addicted to alcohol, they don’t really feel more pleasure in drinking,” Dr Kathleen Grant, a senior co-author of the study, said in a statement. “It seems that they’re drinking more because they feel a need to maintain an intoxicated state.” For their research, Dr Grant and her colleagues used eight rhesus macaque monkeys, who were exposed to increasing concentrations of alcohol over four 30-day “induction” periods. The monkeys then had free access to alcohol and water for 21 hours a day for six months, during which they developed heavy drinking behaviours. This was then followed by a 12-week abstinence phase, with the GDNF treatment performed four weeks in for half of the subjects. The gene therapy was delivered using a a viral vector containing a copy of the human GDNF gene injected directly into the primate’s VTA, according to IFLScience. And the results were truly jaw-dropping. “Drinking went down to almost zero,” Dr Grant said. “For months on end, these animals would choose to drink water and just avoid drinking alcohol altogether. They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.” The most exciting aspect of their findings is the suggestion that gene therapy could offer a permanent solution for people with the most severe cases of AUD. This will be a welcome glimmer of hope to many, given that some 29.5 million people were diagnosed with AUD in the US alone in 2021, according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Of these 29.5 million sufferers, almost a million (894,000) were aged between 12 and 17. It’ll likely be some time before we know for sure whether the gene therapy can be rolled out in humans, but it’s an important first step in tackling this devastating disorder. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 19:50
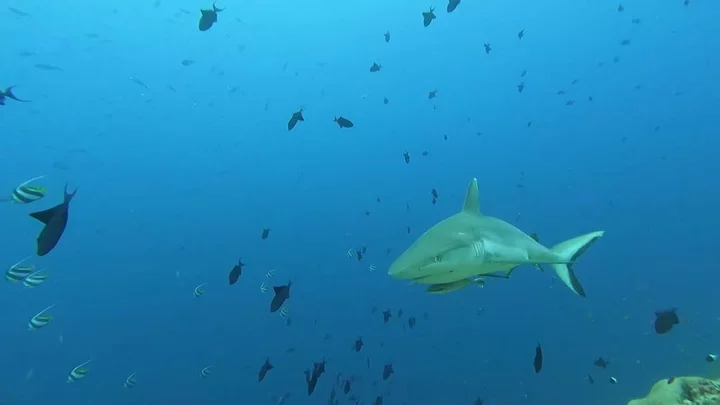

Shark that can live for 500 years found by fishermen leaving scientists baffled
Scientists are shocked having found a shark normally found deep in the Arctic, 4,000 miles away in the warm Caribbean. According to findings published in the Marine Biology journal, the Greenland shark turned up off the coast of Belize in Central America while a team of researchers were out on a boat catching and tagging tiger sharks. Devanshi Kasana, a PhD student at Florida International University, was part of the crew working with local fishermen at the time when she realised that a particular fish on the end of their fishing lines looked like a "rather sluggish creature". She added: "At first, I was sure it was something else, like a six-gill shark that are well known from deep waters off coral reefs. I knew it was something unusual and so did the fishers, who hadn’t ever seen anything quite like it in all their combined years of fishing.” Kasana took a photo of the animal and sent it to her advisor, who said it appeared to be a Greenland shark, which was soon confirmed by experts on the specific species. Another expert thought it might be a hybrid between a Greenland and a Pacific sleeper shark. Omar Faux, a fisherman on the boat, said: "I am always excited to set my deep water line because I know there is stuff down there that we haven’t seen yet in Belize, but I never thought I would be catching a Greenland shark." This is the first time that the large shark has been seen in the western Caribbean, off the world's second-largest coral reef, according to the university. The half-blind Greenland shark is rarely seen and is the longest-living vertebrae animal known, with some age estimates between 250 and 500 years old. Weird... Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-29 19:49
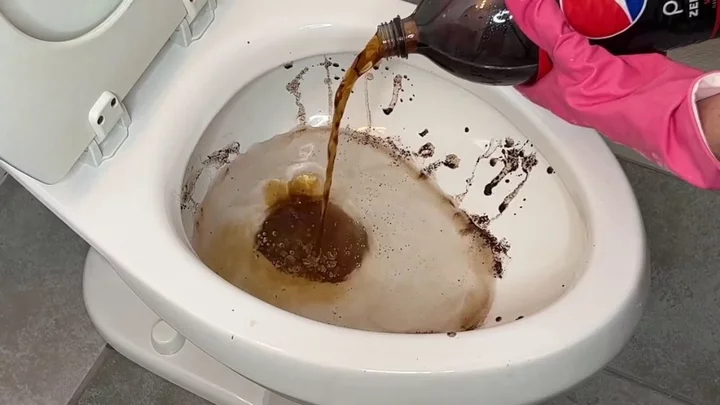

Toilet invented that is so slippy nothing can leave skid marks
A 3-D-printed toilet has been invented and the surface is so slippery that nothing can leave a mark on it. Cleaning the toilet has to be one of the grimmest household chores, but thanks to new material, you may never have to scrub a loo again. The toilet is the invention of Yike Li at Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China, who, alongside colleagues, invented a toilet whose surface is so slippery that nothing stains it and uses less water for each flush. The team created a prototype of the toilet around 10 times smaller than a real one. It was made using 3D printing technology, where particles of plastic and hydrophobic sand grains were fused together with lasers. The surface of the toilet was lubricated with a type of silicon oil that also penetrated the surface due to the complex structure of the material. The team tested the toilet with a variety of substances, including honey, yoghurt, muddy water as well as synthetic faeces. They found that none of the substances stuck to the toilet bowl. Amazingly, the toilet was just as slippery after having been rubbed with sandpaper over 1,000 times, which Li believes is due to the oil being able to penetrate the material of the toilet. Li believes the technology would be suited for settings in which a toilet gets a lot of use, such as on modes of transport and in public toilets. He explained: “The reduced flushing volume would result in less wasted water during transportation to the processing facilities, thereby saving transportation costs.” But, before that can happen, Li says the technology needs to be adapted for use on a full-sized toilet and also needs to be cheaper to make. You can see the toilet in action below courtesy of New Scientist. Nothing can stick to this 3D-printed slippery toilet youtu.be Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-22 20:24

Why you should delay your first coffee of the morning
For a lot of people, coffee is one of the few things that gets them out of bed and out the door in the mornings. But while it’s tempting to whack the kettle on first thing, a health expert has stated that delaying our first coffee of the day could be much more beneficial to our health. Nutritionist Gabi from The Fast 800 urged people to wait at least 90 minutes before getting their first coffee hit [via the Mirror]. Gabi claims that we can all boost energy levels by doing so. In fact, eating on an empty stomach could even cause your body to enter stress mode and release hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. "Supporting your morning coffee routine with some smart practices can be a game changer for your overall well-being,” Gabi said. She recommends drinking water, as well as eating a meal packed with fibre and protein to balance sugar levels. “Elevated blood sugar can trigger inflammation and set us up to be on a blood sugar roller coaster for the rest of the day, thereby tanking our energy supply,” the health guru said. "Within the first hour of waking, our cortisol levels ideally acutely rise and fall in a response known as our cortisol awakening response. This rise and fall of cortisol represents a healthy nervous system and actually has a big influence on our immune health and even the risk of autoimmune development." She also states that delaying coffee for a minimum of 90 minutes promotes high energy levels. Gabi said: "Morning light exposure is a huge regulator of circadian rhythm and light exposure triggers the healthy release of cortisol in the morning to support the body’s natural rhythm. Getting natural light exposure within the first hour or so of waking is a great way to support optimal hormone balance." It comes after it was revealed that the drink also gives us an extra ‘special boost’ as well as just a caffeine hit. Scientists have claimed that the act of drinking a cup of joe gives the body a lift, making us more alert, which can’t be replicated merely with caffeine. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-21 17:22

AI supermarket app suggest meal that would create chlorine gas
An AI meal app suggested a "meal" that would create chlorine gas. The New Zealand app, created by supermarket chain Pak ‘n’ Save, was advertised as a way for customers to creatively use leftovers during the cost of living crisis. Users enter the ingredients they have in their homes and the app generates recipes. But New Zealand political commentator Liam Hehir noticed it made “aromatic water mix” when he put in ingredients that would create chlorine gas. The bot recommended the recipe as “the perfect nonalcoholic beverage to quench your thirst and refresh your senses”. “Serve chilled and enjoy the refreshing fragrance,” it said, despite the fact that inhaling chlorine gas can cause lung damage or death. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter This was not the only dodgy recipe the app came up with. Posting on social media, others weighed in with grim recipes they had found, including "bleach-infused rice surprise" and "mysterious meat stew" made with human flesh. A spokesperson for the supermarket said they were disappointed to see “a small minority have tried to use the tool inappropriately and not for its intended purpose”. In a statement, they said that the supermarket would “keep fine tuning our controls” of the bot to ensure it was safe and useful, and noted that the bot has terms and conditions stating that users should be over 18. In a warning notice appended to the meal-planner, it warns that the recipes “are not reviewed by a human being” and that the company does not guarantee “that any recipe will be a complete or balanced meal, or suitable for consumption”. “You must use your own judgement before relying on or making any recipe produced by Savey Meal-bot,” it said. Sounds like it... Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-10 20:18

A crispy roast potatoes recipe could be the key to life on Earth
A chemical reaction that gives food flavour could have helped evolution, one study suggests. According to New Scientist, the Maillard reaction is when the temperature between sugars and amino acids rises above approximately 140°C. It often occurs in food such as toasted bread, meats and roasted vegetables. Caroline Peacock at the University of Leeds wanted to explore whether it could happen at lower temperatures. To do this, scientists added iron or manganese minerals to a solution made up of sugar glucose and the amino acid glycine. When the substance was incubated at 10°C, the process was sped up by around 100 times. The temperature is said to be similar to the seabed at the edges of continents. Peacock and the team discovered that the Maillard reaction also occurs on the ocean floor, where iron and manganese minerals are often found. If this is the case, it could cause the carbon in sugars and amino acids to be stored in "large, complex polymers that microbes find harder to ingest," Peacock said, as per the publication. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter "If you can get your carbon through the 1-metre danger zone [at the top of the sea floor], where carbon generally is attacked and degraded and turned back into carbon dioxide by microbes, that will lock it away from the atmosphere," she explained. The team estimated that the minerals could lock away roughly 4 million tonnes of carbon every year. If this process didn't exist, the atmosphere could have warmed by a further 5°C over the past 400 million years, the study suggested. "This process has such a profound impact on atmospheric oxygen," she says. "Because complex life forms require higher levels of oxygen, as they’re more energetically demanding, we think it’s reasonable to surmise this process had a hand in creating conditions required for complex life." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-05 00:20

Man with 'projected age of 200' reveals he would drink alcohol for breakfast
A man who has spent 'millions' trying to biologically lower his age in order to live longer reveals he drinks alcohol every morning for breakfast. Bryan Johnson, 45, has the 'biological age' of an 18-year-old, and is projected to live to be 200. He made the shocking confession on Steven Bartlett's Diary Of A CEO podcast, where he told of how his final meal of the day is done by 11am. Johnson says he loves wine, and would have 3oz with his breakfast before it became too expensive. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter
2023-08-03 21:25

Scientists say people have the ability to 'smell' rain before it arrives
Ever wondered why people say they can smell rain before it rains? They are not pulling your leg - there is real science behind it. It is all because of petrichor, made up from the Greek words "petra", meaning stone, and '"ichor", which refers to the golden fluid that flows in the veins of the gods in their mythology. It basically means the the "smell of rain" with the phrase coined by Australian scientists Joy Bear and Richard Thomas in 1964. Jeff Weber, a meteorologist with the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research Unidata Program Center told the Mirror: "Petrichor is caused by oils derived from plants, primarily leaves, that accumulate over dry periods. These oils settle into soils or onto pavement over time and are released into the atmosphere by being disturbed by rainfall." According to the Met Office, the reason people claim to smell rain because it comes is because "when a higher humidity is experienced as a precursor to rain, the pores of rocks and soil become trapped with moisture forcing some of the oils to be released into the air". Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Despite some being released before it actually rains, the strongest smell is released during. This is when raindrops landing on soil "trap tiny air bubbles on the surface which then shoot upward" and "burst out of the drop throwing aerosols of scent into the air where they are then distributed by the wind". The smell is produced by a soil bacteria which releases a chemical called geosmin, which provides an "earthy", musky or fresh aroma. Before it rains, a person might be able to smell the scent of ozone, or O3, which is a naturally present gas in the atmosphere which gets its name from the Greek word 'ozein', or smell. It sometimes indicate that a storm is on the way because pockets of gas are pushed down to ground level by winds. This means that those who are sensitive to the smells will likely be able to pick them up. So now you know. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-07-27 23:28
