
Who is Elizabeth Seibert? Model faces backlash for her strict diet of consuming 3,000 calories in 3-hour eating window
Alongside her high-fat breakfast, Elizabeth Seibert claims to take 32 vitamin pills as she has a 'lot of nutrient deficiencies'
2023-08-05 18:16

Black Friday Deals at Amazon's Outlet: $180 Beats Headphones
We have a secret to tell you, but you have to promise to share it
2023-11-25 02:16
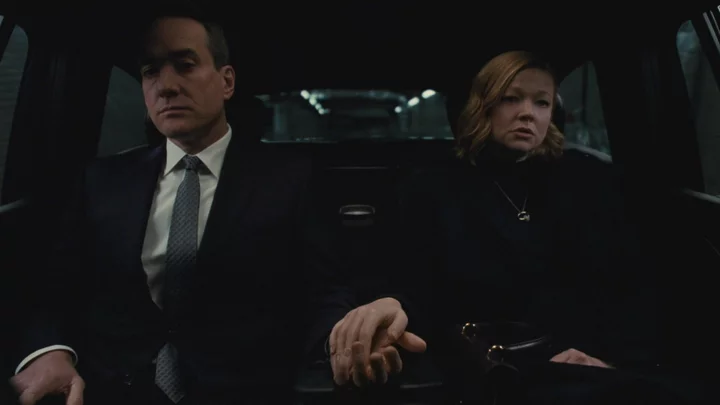

This 'Succession' line gave a sneaky clue as to who would end up as CEO
Succession is over, and a new king has been crowned. And while Tom Wambsgans (Matthew
2023-05-30 19:17
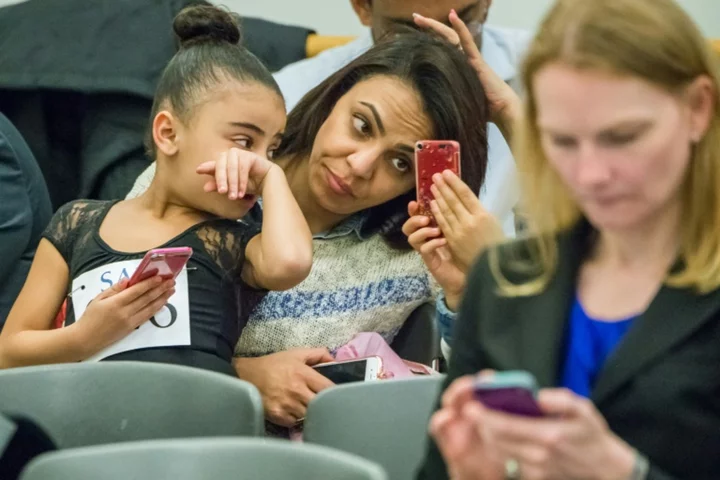

In US, lack of affordable child care hinders work force
Parents of young children in the United States are finding that with day care centers in short supply, or too expensive, more and more of them -- mostly mothers -- are having to stay at...
2023-10-06 09:59
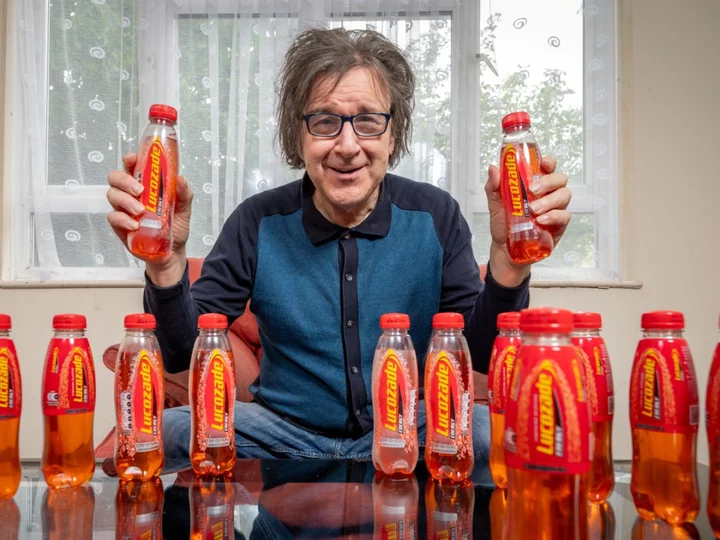

Lucozade addict drinks eight bottles a day and says it’s harder to quit than class-A drugs
A grandfather is addicted to Lucozade despite having three heart attacks, and said it's harder to give up than class-A drugs. Garry Johnson, 65, began drinking coffee aged 12 and loved the caffeine buzz. The now-retired painter and decorator took cocaine and amphetamines in his teens, and after 15 years of on-off drug use went “cold turkey” when his son Sam was born in 1992. Keen to stay energised, he took up drinking 380ml bottle bottles of Lucozade Original, and now gets through eight a day. He's had the habit for 29 YEARS and it currently costs him around £150 a month. And at today's prices, his nearly three decade habit would have cost him more than £42,800. He had three heart attacks between 2012 and 2014 because of a hereditary heart condition, and doctors encouraged him to ditch caffeinated drinks. He gave up dairy and every other form of caffeine - but he still necks more than three litres of Lucozade a day. He said Lucozade is proving harder to give up than class-A drugs - because of the "after effect - like that lovely feeling in your mouth after you eat an expensive bit of chocolate." Garry, from Basildon, Essex, said: "I took cocaine every day but it was a piece of cake to give up - but I'd find it really hard to ever give up Lucozade. "I love it - not just the taste but the affect on my body makes me feel great. If I do go two or three hours without one, I fancy one... God knows how I'd be after two days.” He stopped using cocaine aged 30, when his son Sam, now 31, was born and went cold turkey because being a new dad was "stimulant enough". He started drinking Red Bull but found himself with migraines, and eventually moved onto Lucozade. He initially drank six a day, but has had eight a day for the last seven years. Now he goes to Tesco every day and buys one or two four-packs - depending how many bottles he already has stacked up in the fridge ready to drink. "I've always needed some kind of stimulant and eventually I realised Lucozade is perfect for me," he said. "After my heart attacks they told me to quit the energy drinks but I recently had new heart tests and my results are better than they've ever been. "I guess I've just found one that suits my body." But Garry said he doesn't even want to give up because it's a "part of his identity" - like a person's favourite shirt or their daily breakfast. He justifies the cost because he doesn't drink alcohol or smoke. He said: "£5 a day - that's less than a pint of beer today in some places." If you or someone you know is suffering from alcohol addiction, you can confidentially call the national alcohol helpline Drinkline on 0300 123 1110 or visit the NHS website here for information about the programmes available to you. If you or someone you know is suffering from drug addiction, you can seek confidential help and support 24-7 from Frank, by calling 0300 123 6600, texting 82111, sending an email or visiting their website here. SWNS Read More What I gained (and lost) by walking 10,000 steps each day for 5 months Husband ‘ruins’ dinner because of his wife’s typo: ‘The worst kind of control freak’ John Whaite says he ‘spent time apart’ from fiancé after ‘falling in love’ with Strictly pro
2023-08-14 14:45

Your 2023 Halloween Horoscope By Zodiac Sign Is Here
This Halloween brings lots of ghastly fun our way. The lunar eclipse in Taurus wraps up on October 28, so the energy around Hallow’s Eve should illuminate matters in our lives, as well as shaking up our personal circumstances and relationships. With Venus in Virgo and Uranus retrograde in Taurus harmonizing, we’ll want to step out of our comfort zones and be present in the moment. The cosmos is bringing both tricks and treats our way, due to the duplicitous and dualistic Gemini Moon. The following morning, on All Saints Day and Dia de Los Muertos, the moon creates a T-Square with Venus in Virgo and Neptune retrograde in Pisces, heightening our intuition and connection with the spiritual world. Grab your black salt to protect your home from unwanted energy and create an altar to honor your ancestors.
2023-10-25 19:59

Lando Norris endures heavy crash at start of Las Vegas Grand Prix
Lando Norris was an early retirement from the Las Vegas Grand Prix after a heavy crash into the wall. The McLaren driver, who only started 15th on the grid after a disappointing qualifying, lost control of his car at turn 12. The Brit diverted right, straight into the wall and losing a tyre, before spinning into the barrier. Norris, while breathing heavily, did let his engineer know “I’m OK.” More to follow… Read More F1 Las Vegas Grand Prix LIVE: Race updates and times in Sin City What Charles Leclerc needs to claim victory from pole in first Las Vegas Grand Prix Charles Leclerc lights up Las Vegas to claim pole position for Ferrari
2023-11-19 14:54

Who is Jaime Christine Major? Burger King worker faces 20 years in prison for serving fries from trash can
Burger King's corporate office informed the authorities that Major had been dishing out fries from the garbage bin
2023-07-20 18:54

How women squirt on camera, according to porn stars
In porn, squirting (or female ejaculation) is often so theatrical that it’s a centerpiece of
2023-08-30 18:29
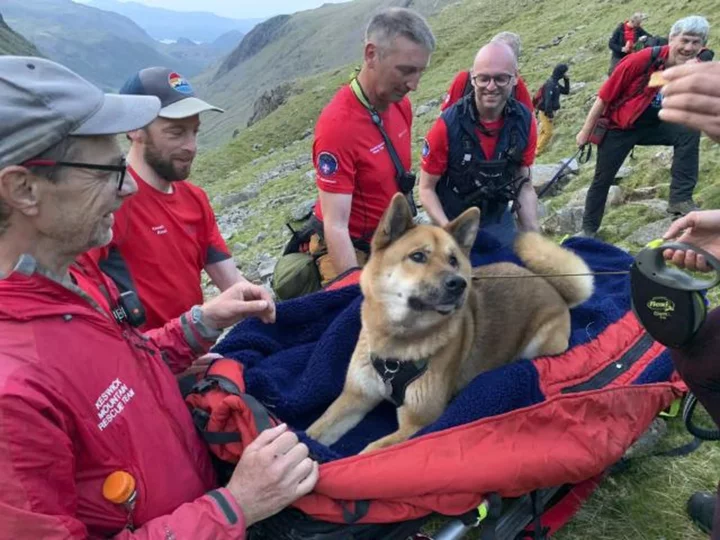

'Exhausted' dog rescued after scaling England's highest mountain
A 13-strong rescue team has rescued an "injured and exhausted" dog from England's highest mountain in an operation lasting more than four hours.
2023-05-16 19:45

US Capital Area Braces for Economic Hit From Government Shutdown
The Washington, DC region is bracing for disruption to the local economy when federal funding lapses at midnight
2023-09-29 22:59
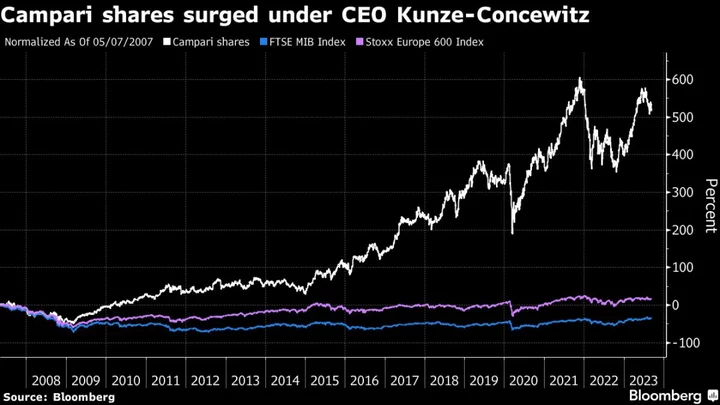
Campari Shares Surged More Than 520% Under Retiring Veteran CEO
Spirits maker Campari saw its shares rise more than 520% under the 16-year tenure of retiring Chief Executive
2023-09-12 19:47
You Might Like...

PJT Hires Ex-Centerview Banker Phillips for Consumer M&A
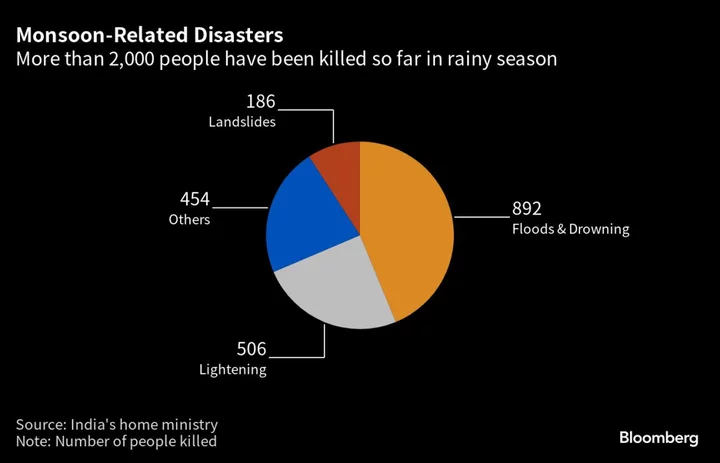
India Braces for More Rain After Floods, Lightening Kill 2,000
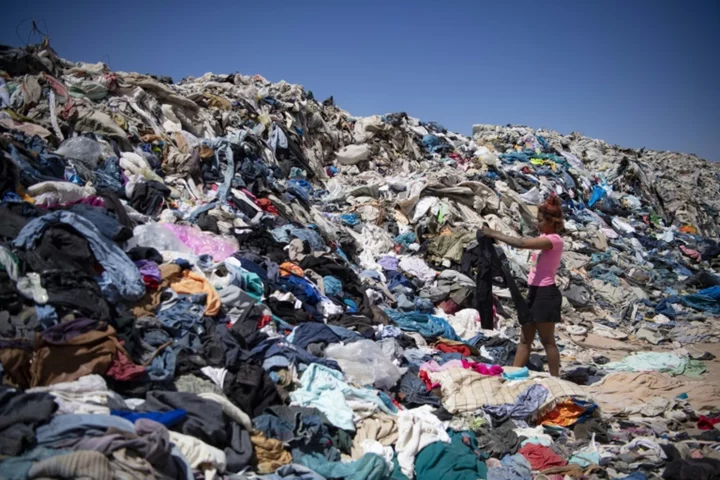

Six recycling innovations that could change fashion
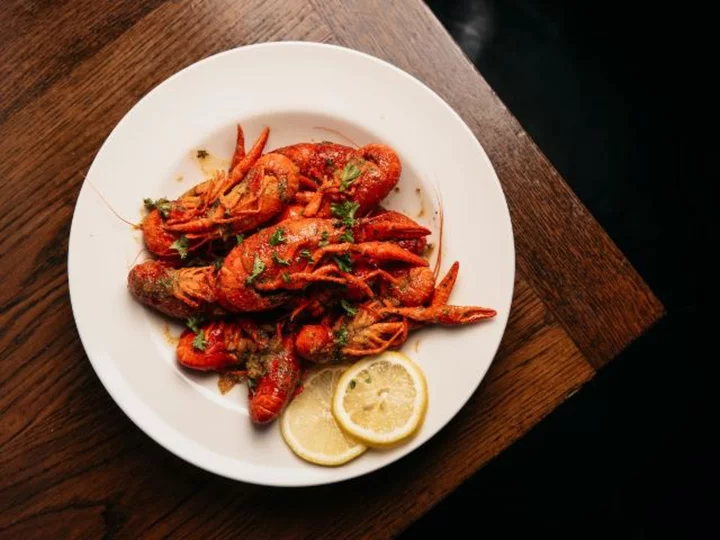

These Asian fusion cuisines tell an American story
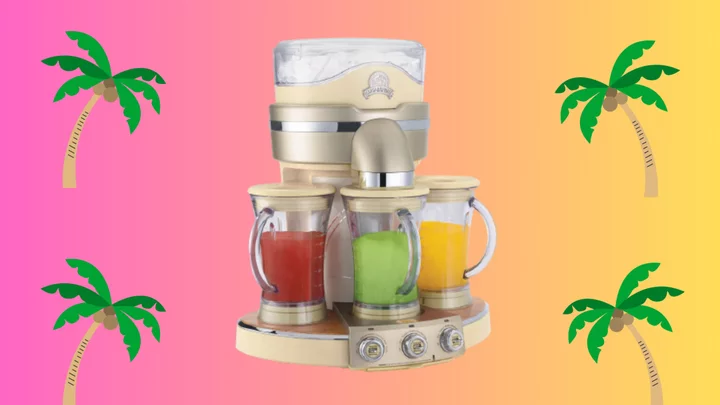

Embrace the island life with $300 off a Margaritaville Frozen Concoction Maker

I Finally Reached All My NYC Dreams — But The Struggle Was Real
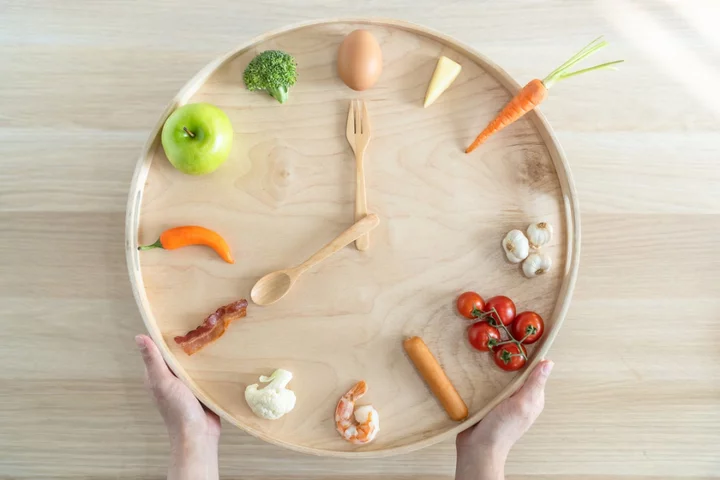

The exact time Brits find themselves ‘uncontrollably hungry’ revealed

CoreMedia Strengthens Digital Experience Capabilities with Acquisition of BySide and Smarkio
