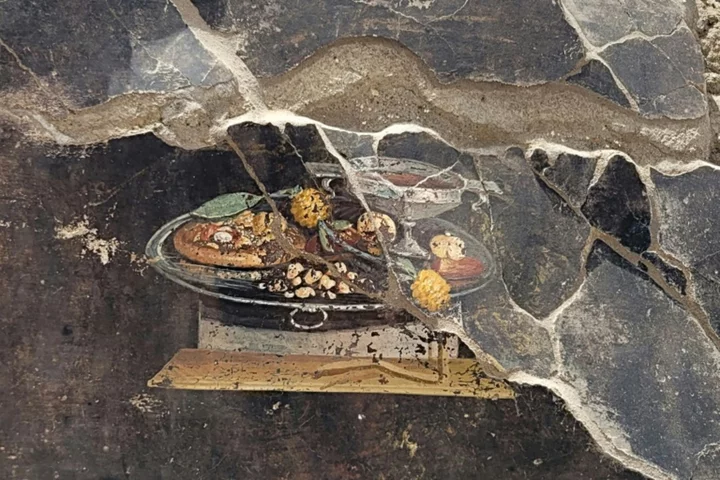

Pompeii fresco shows pizza precursor -- but hold the cheese
Even the ancient Romans liked their...
2023-06-27 19:24

Lewis Hamilton warned not to expect instant results from Mercedes upgrade
Toto Wolff has warned Lewis Hamilton that Mercedes’ upgrade is unlikely to provide a swift end to his losing streak. Hamilton and team-mate George Russell were given their first taste of the team’s revamped machine in Monaco. Hamilton and Russell qualified sixth and eighth, before making up two and three places respectively in Sunday’s rain-hit race following an early call to move from slick to wet rubber. Traditionally, the Monte Carlo layout has been among Mercedes’ worst tracks with this weekend’s race at the Circuit de Catalunya in Barcelona set to represent a truer reflection of the team’s outright speed. But Wolff believes he did not see enough progress from their upgraded car to suggest they will immediately move ahead of Aston Martin and Ferrari in the pecking order, or challenge Max Verstappen’s Red Bull team who have won all six races this year. “We need to be careful,” said team principal Wolff. “We will collect more data in Barcelona, but I don’t expect us to clear Ferrari and Aston Martin there either. “It is about understanding what does this car do now and how do we set it up? “We are good at grinding away. Last year, the package was terrible at the beginning of the season, and we won a race in Interlagos [at the penultimate round] so we will get there.” Hamilton finished 39 seconds behind Verstappen on Sunday as the Dutchman claimed his fourth victory in six races to extend his championship lead to 39 points. Red Bull have now won 15 of the last 16 grands prix, with Verstappen, who grazed the wall en route to taking the chequered flag in Monte Carlo, remaining on course to race to his third world title in as many years. Asked if Verstappen’s dominance is proving to be a turn-off for the sport, Wolff replied: “When you win in Formula One it is a meritocracy. “They have done a good job and the car is fast in all conditions and the driver is at the top of his game. “We need to do a better job, catch up, find intelligent solutions and hope our development slope is steeper than theirs, and eventually fight again. “Whether it is good for the show or not, a strong fight between 10 drivers, or at least two, is obviously much better for all of us, but we have to accept it and work to get back there. “The best driver in the best car spending the same money wins the championship, and if you break the rules you should be heavily penalised, but only then, and you should not be penalised for simply doing a good job.” Read More Concerns Monaco GP could be ‘left behind’ as Max Verstappen wins ‘boring race’ Wolff fumes as Hamilton’s F1 car floor displayed during removal from Monaco track Fernando Alonso ready to pounce if Max Verstappen makes a slow start in Monaco Max Verstappen fends off Fernando Alonso to take pole position in Monaco Lewis Hamilton reveals impact of Mercedes updates in Monaco F1 2023 calendar: Every race this season
2023-05-29 20:53

Grab this refurbished 4th gen Echo at an all-time low price
SAVE $50: As of October 19, a certified refurbished 4th gen Echo is on sale
2023-10-19 23:26

Coca-Cola Beverages Florida Executive Jason Reed Elected Chairperson of the Coca-Cola System’s National Product Supply Group Board of Directors
TAMPA, Fla.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 1, 2023--
2023-06-02 03:47

Kimberly Palmer: How to stay safe from financial scams
While there’s no way to guarantee you’ll completely avoid financial scams, there are steps you can take to reduce your chances of falling for one
2023-07-31 23:16
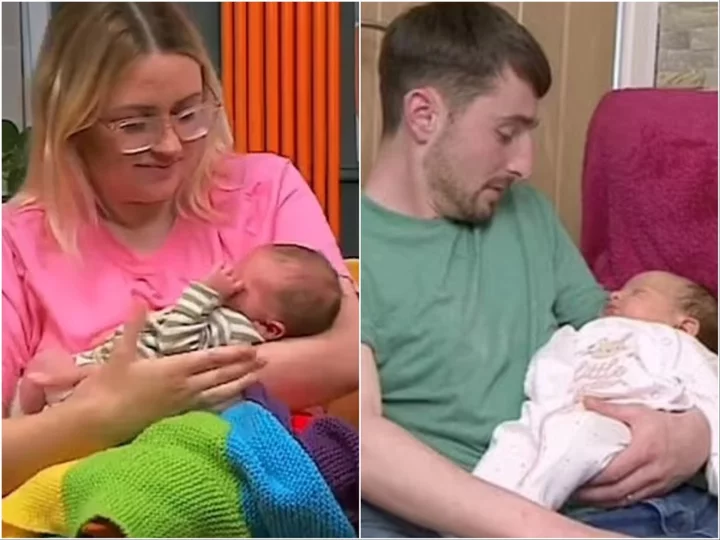

Gogglebox’s Ellie Warner announces newborn son while co-star Pete Sandiford welcomes baby girl
Gogglebox star Ellie Warner has announced that she has given birth to a son she shares with her boyfriend Nat Eddleston, while co-star Pete Sandiford and his wife Paige Yeoman have welcomed a newborn girl. Both new parents confirmed the arrivals while appearing on Friday’s (2 June) episode of the Channel 4 show, giving viewers a glimpse at the children. Warner, 32, introduced her newborn as she handed the baby to her sister Izzi. Later, she shared a picture of her son on Instagram, who she has named Ezra. The picture sees baby Ezra sleeping in a cot underneath a yellow blanket. She wrote: “Sweet baby Ezra, he has made our lives complete, we love you so much son.” Meanwhile, Sandiford also confirmed his wife Paige Yeoman has given birth to their second child, a baby girl, on Friday’s show. Appearing on the segment with his sister Sophie, Sandiford is seen holding his baby, before saying to Sophie: “Did I tell you her full name? We think we’re going to call her Evie Sylvie Sandiford.” Sandiford and his wife Paige welcomed their first son Jimmy in August 2021 and wed last year. Announcing his baby news, Sandiford told his son Jimmy in a sweet clip that he was about to become a big brother. He joked: “Jimbers, you’re going to have a little brother or sister coming. You’re going to have to milk it.” Hairdresser Warner confirmed she and boyfriend Nat were expecting their first child together back in December. She confirmed her pregnancy on a Gogglebox episode, appearing alongside her sister Izzi, to who she showed her ultrasound scan. Warner, who has been dating her boyfriend Nat Eddleston since 2018, reflected on the moment she showed her mother her pregnancy scan. “When I showed mum the picture she said, ‘Oh can I take a picture,’ and you didn’t even look at it for two minutes,” she said. Izzi responded: “I did! I told you where the things were, I’ll stare at it a bit longer just to make you happy.” Warner and her sister Izzi first appeared on Gogglebox in 2015 after Warner was reportedly approached by a friend who worked on casting for the show. Sandiford and his sister have been fan favourites since they joined the show in 2017. Read More Triathlete proudly shares ‘beautiful’ racing photo where she bled through swimsuit while on her period A Place In The Sun’s Jonnie Irwin admitted to hospital amid terminal diagnosis Prince William overheard telling Kate to ‘chop chop’ at Jordan royal wedding Sarah Beeny shares health update after all-clear from breast cancer Meet the unconventional couple behind Escape to the Chateau Vanessa Feltz shares horrifying Rolf Harris encounter during live interview
2023-06-03 18:54

Update New or Used Gear With Windows 11 Pro, now under $23
Gifting a loved one a new or refurbished laptop or computer is both practical and
2023-11-30 00:54
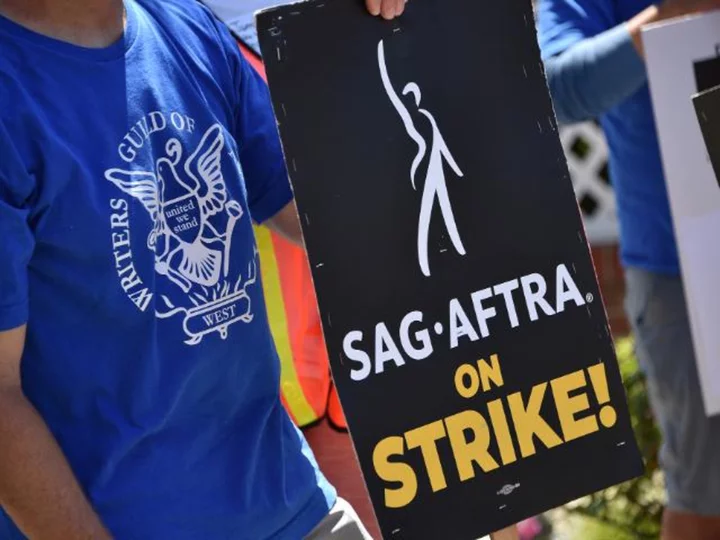

They don't act or write, but the Hollywood strikes are putting them out of work
On Saturday, a group of set and prop warehouse owners are getting together for a "Crewlateral Yard Sale," hoping to make a few bucks selling inventory while orders for movie and TV sets have come to a complete halt over the last two months.
2023-07-22 19:18

Reddit's API protest just made John Oliver a special job offer
Over on Reddit, the protest continues. It's been almost a month now since thousands of
2023-07-11 18:53

Elmhurst® 1925 Announces Its Newest Seasonal Offering, Apple Pie Spice Seasonal Blend, Alongside Returning Fan Favorite LTOs
ELMA, N.Y.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 28, 2023--
2023-08-28 20:23

Indigenous rights supporters rally across Australia before vote
Australians rallied around the country on Sunday to fight for a landmark Indigenous rights reform that is bleeding support in the polls...
2023-09-17 15:24

What's streaming now: Ed Sheeran, 'The Voice,' 'The Golden Bachelor' and Wes Anderson returns
This week’s new entertainment releases include an album from Ed Sheeran centered on his relationships, a spinoff of “The Bachelor” starring a 72-year-old widower and Wes Anderson returns for a second time this year with “The Wonderful Story of Henry Sugar” starring Benedict Cumberbatch
2023-09-29 12:16
You Might Like...

How Long Will It Take to Charge Your iPhone? Use This Shortcut to Find Out

Express CEO Tim Baxter resigns amid declining revenue

Class-Action Suit Goes After H&R Block, Google, Meta for Alleged Tax Data Sharing

Looking for a house? High mortgages, few homes lead to biggest annual sales drop in 11 years
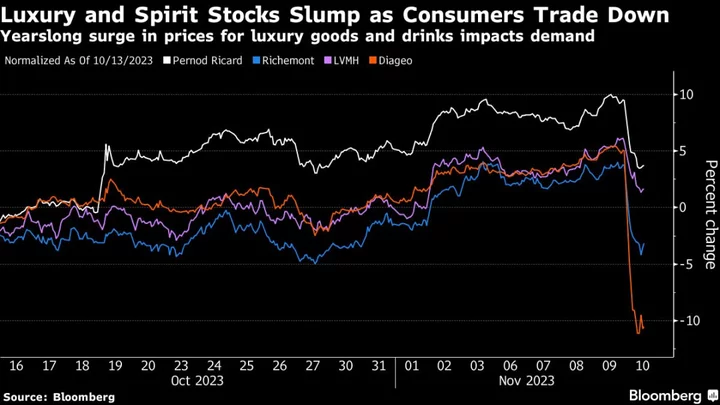
Spirits and Luxury Stocks Fall as Pricing Power Starts to Fade

Get this refurbished iPad with accessories for $280

These Are The 5 Top K-Beauty Skincare Ingredients, According To An Expert
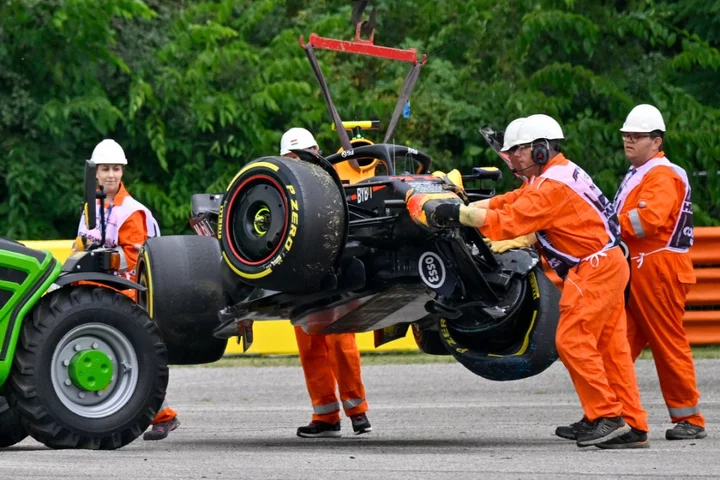

More woe for Sergio Perez as Red Bull driver crashes out of practice in Hungary
